Leptothorax pocahontas
Leptothorax pocahontas (Powhatan: pocahontas = playful one) is a threatened species of ant endemic to Alberta, Canada,[2] facing a high risk of extinction.
| Leptothorax pocahontas | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | L. pocahontas |
| Binomial name | |
| Leptothorax pocahontas (Buschinger, 1979) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Doronomyrmex pocahontas | |
The total length of a female ant, including the mandibles is 4 mm.[2] The chromosome number of the species is n = 18.[3]
The species is known only from its type locality,[3] Maligne Canyon, near Jasper, Alberta, Canada.[2]
It closely resembles the workerless European species, Leptothorax pacis, and having believed to be also lacking a worker caste when it was first described in 1979, was placed in the same genus (at the time, genus Doronomyrmex).[2]
The queen is highly polymorphic, differing in size, pilosity, sculpture (shininess) and colouration.[3]
The genus Doronomyrmex was synonymized with Leptothorax as a junior synonym by Heinze (1998),[4] a taxonomic action later supported by Bolton's (2003)[5] "Classification and Synopsis of Formicidae". Thus all species previously included within the genus Doronomyrmex taxon should be technically considered to belong to Leptothorax until the next taxonomic revision.
Conservation status
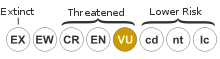
The IUCN Red List lists the species as fitting the "D2" criteria of the Vulnerable (VU) category in the "1994 Categories & Criteria", meaning the population has an acute restriction in its area of occupancy (typically less than 100 km2) or in the number of locations (typically less than five). As such, the population is prone to the effects of human activities, or chance events and may become critically endangered or may even become extinct very suddenly. The last assessment of its extinction risk was published by the World Conservation Union (IUCN) in 1996.[1]
References
- Social Insects Specialist Group (1996). "Doronomyrmex pocahontas". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 1996: e.T6811A12808387. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T6811A12808387.en.
- Buschinger, A. 1979. Doronomyrmex pocahontas, n. sp., a parasitic ant from Alberta, Canada (Hym. Formicidae). Ins. Soc. 26: 216-222.
- Buschinger, A. and J. Heinze. 1993. Doronomyrmex pocahontas: not a workerless parasite but still an enigmatic taxon (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Ins. Soc. 40: 423-432.
- Heinze, J. 1998 ("1995"). The origin of workerless parasites in Leptothorax (s. str.) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Psyche 102: 195-214.
- Bolton, B. 2003. Synopsis and classification of Formicidae. Memoirs of the American Entomological Institute 71: 1-370.