Lemko Republic
Lemko-Rusyn People's Republic (Lemko: Руска Народна Република Лемків / Ruska Narodna Respublika Lemkiv), often known as the Lemko-Rusyn Republic or the Lemko Republic, was a short-lived state, founded on 5 December 1918 in the aftermath of World War I and the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire.[1] It was centered on Florynka, a village in the south-east of present-day Poland (on the border with Slovakia, south and south-east of Nowy Targ - Florynka, Krynica-Zdrój, Świetnica, Gładyszów, Sanok). Being Russophile, its intent was unification with a democratic Russia and was opposed to a union with the West Ukrainian People's Republic. A union with Russia proved impossible, so the Republic then attempted to join Subcarpathian Rus' as an autonomous province of Czechoslovakia. This, however, was opposed by the then governor of Subcarpathian Rus', Gregory Žatkovich.
Lemko-Rusyn People's Republic Ruska Narodna Respublika Lemkiv | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1920 | |||||||||
 Flag | |||||||||
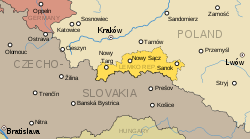 Territory claimed by the Lemko-Rusyn Republic (yellow color) | |||||||||
| Capital | Florynka | ||||||||
| Common languages | Lemko dialect | ||||||||
| Government | Republic | ||||||||
| President | |||||||||
• 1918-1920 | Jaroslav Kacmarcyk | ||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||||||
• Established | 5 December 1918 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | March 1920 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
The Republic was headed by Jaroslav Kacmarcyk as President of the Central National Council. It was ended by the Polish government in March 1920. Its fate was sealed by the September 1919 Treaty of Saint-Germain, which gave Galicia west of the San to Poland[2] and by the Peace of Riga in March 1921 whereby the fait accompli was recognized by Moscow.
This state should not be confused with the Komancza Republic of eastern Lemkivshchyna, another short-lived republic. This was a smaller pro-Ukrainian state that existed between November 1918 and 23 January 1919.
Territory
On 5 December 1918, the Republic's delegates issued the statement: "We, the Rusyn nation, living in a compact settlement in the southern parts of the Galician administrative units of Nowy Targ and in Sanok. Do not wish to be incorporated into the Polish state, and wish to share the fate of our Rusyn brothers [living] in Spiš, Šariš, and Zemplín counties as one indivisible geographic and ethnographic unit."[3]
See also
Notes
- Magocsi, Paul Robert (Fall 1993). "The Ukrainian question between Poland and Czechoslovakia: The Lemko Rusyn republic (1918-1920) and political thought in western Rus'-Ukraine". Nationalities Papers. 21 (2): 95–103. doi:10.1080/00905999308408278.
- Magocsi, Paul Robert (2002) [1993]. "Central Europe 1918-1923". Historical Atlas of Central Europe. A History of East Central Europe. 1 (revised and expanded ed.). Seattle: University of Washington Press. p. 127. ISBN 0-295-98146-6. OCLC 47097699.
- Horbal, Bogdan (1997). Działalność polityczna Łemków na Łemkowszczyźnie 1918–1921 [Political activity of the Lemkos in Lemkivshchyna 1918–1921] (in Polish). Wrocław: Wydawn Arboretum. p. 45. ISBN 978-83-86308-22-4. OCLC 37645527.
External links
- History of the Lemko-Rusyn Republic
- Paul R. Magocsi article on the Lemko Republic
- (in Polish) Ćmiech, Andrzej (14 November 2008). "Państwo w państwie Ruska Ludowa Republika Łemków" [State of the state]. Gazeta Gorlicka. Retrieved 24 May 2010.