Laser flash analysis
The laser flash analysis or laser flash method is used to measure thermal diffusivity of a variety of different materials. An energy pulse heats one side of a plane-parallel sample and the resulting time dependent temperature rise on the backside due to the energy input is detected. The higher the thermal diffusivity of the sample, the faster the energy reaches the backside. A state-of-the-art laser flash apparatus (LFA) to measure thermal diffusivity over a broad temperature range, is shown on the right hand side.
| Uses | to measure thermal diffusivity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, |
|---|---|
In a one-dimensional, adiabatic case the thermal diffusivity is calculated from this temperature rise as follows:
Where
- is the thermal diffusivity in cm²/s
- is the thickness of the sample in cm
- is the time to the half maximum in s
Measurement principle
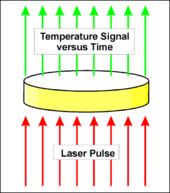
The laser flash method was developed by Parker et al. in 1961.[1] In a vertical setup, a light source (e.g. laser, flashlamp) heats the sample from the bottom side and a detector on top detects the time-dependent temperature rise. For measuring the thermal diffusivity, which is strongly temperature-dependent, at different temperatures the sample can be placed in a furnace at constant temperature.
Perfect conditions are
- homogenous material,
- a homogenous energy input on the front side
- a time-dependent short pulse – in form of a Dirac delta function
Several improvements on the models have been made. In 1963 Cowan takes radiation and convection on the surface into account.[2] Cape and Lehman consider transient heat transfer, finite pulse effects and also heat losses in the same year.[3] Blumm and Opfermann improved the Cape-Lehman-Model with high order solutions of radial transient heat transfer and facial heat loss, non-linear regression routine in case of high heat losses and an advanced, patented pulse length correction.[4][5]
References
- W.J. Parker; R.J. Jenkins; C.P. Butler; G.L. Abbott (1961). "Method of Determining Thermal Diffusivity, Heat Capacity and Thermal Conductivity". Journal of Applied Physics. 32 (9): 1679. Bibcode:1961JAP....32.1679P. doi:10.1063/1.1728417.
- R.D. Cowan (1963). "Pulse Method of Measuring Thermal Diffusivity at High Temperatures". Journal of Applied Physics. 34 (4): 926. Bibcode:1963JAP....34..926C. doi:10.1063/1.1729564.
- J.A. Cape; G.W. Lehman (1963). "Temperature and Finite-Pulse-Time Effects in the Flash Method for Measuring Thermal Diffusivity". Journal of Applied Physics. 34 (7): 1909. Bibcode:1963JAP....34.1909C. doi:10.1063/1.1729711.
- U.S. Patent 7,038,209
- J. Blumm; J. Opfermann (2002). "Improvement of the mathematical modeling of flash measurements". High Temperatures – High Pressures. 34 (5): 515. doi:10.1068/htjr061.