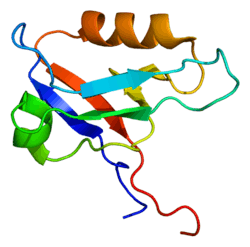
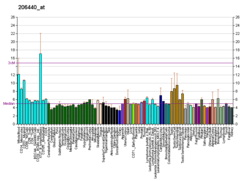
LIN7A
Lin-7 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LIN7A gene.[5][6][7]
Interactions
LIN7A has been shown to interact with:
gollark: Not that the bridge is also an exit node.
gollark: To clarify, I mean the exit node is the thing sending things to my bridge.
gollark: Who doesn't?
gollark: I mean, not really "somehow", it's easy to do. I just wonder why.
gollark: It's a Tor exit node.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000111052 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000019906 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Jo K, Derin R, Li M, Bredt DS (Jun 1999). "Characterization of MALS/Velis-1, -2, and -3: a family of mammalian LIN-7 homologs enriched at brain synapses in association with the postsynaptic density-95/NMDA receptor postsynaptic complex". J Neurosci. 19 (11): 4189–99. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-11-04189.1999. PMID 10341223.
- Bohl J, Brimer N, Lyons C, Vande Pol SB (Mar 2007). "The stardust family protein MPP7 forms a tripartite complex with LIN7 and DLG1 that regulates the stability and localization of DLG1 to cell junctions". J Biol Chem. 282 (13): 9392–400. doi:10.1074/jbc.M610002200. PMID 17237226.
- "Entrez Gene: LIN7A lin-7 homolog A (C. elegans)".
- Leonoudakis D, Conti LR, Radeke CM, McGuire LM, Vandenberg CA (Apr 2004). "A multiprotein trafficking complex composed of SAP97, CASK, Veli, and Mint1 is associated with inward rectifier Kir2 potassium channels". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (18): 19051–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400284200. PMID 14960569.
- Borg JP, Straight SW, Kaech SM, de Taddéo-Borg M, Kroon DE, Karnak D, Turner RS, Kim SK, Margolis B (Nov 1998). "Identification of an evolutionarily conserved heterotrimeric protein complex involved in protein targeting". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (48): 31633–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.48.31633. PMID 9822620.
- Leonoudakis D, Conti LR, Anderson S, Radeke CM, McGuire LM, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Yates JR, Vandenberg CA (May 2004). "Protein trafficking and anchoring complexes revealed by proteomic analysis of inward rectifier potassium channel (Kir2.x)-associated proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (21): 22331–46. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400285200. PMID 15024025.
Further reading
- Rousset R, Fabre S, Desbois C, Bantignies F, Jalinot P (1998). "The C-terminus of the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein mediates interaction with the PDZ domain of cellular proteins". Oncogene. 16 (5): 643–54. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201567. PMID 9482110.
- Butz S, Okamoto M, Südhof TC (1998). "A tripartite protein complex with the potential to couple synaptic vesicle exocytosis to cell adhesion in brain". Cell. 94 (6): 773–82. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81736-5. PMID 9753324.
- Borg JP, Straight SW, Kaech SM, de Taddéo-Borg M, Kroon DE, Karnak D, Turner RS, Kim SK, Margolis B (1998). "Identification of an evolutionarily conserved heterotrimeric protein complex involved in protein targeting". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (48): 31633–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.48.31633. PMID 9822620.
- Borg JP, Lõpez-Figueroa MO, de Taddèo-Borg M, Kroon DE, Turner RS, Watson SJ, Margolis B (1999). "Molecular analysis of the X11-mLin-2/CASK complex in brain". J. Neurosci. 19 (4): 1307–16. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-04-01307.1999. PMID 9952408.
- Perego C, Vanoni C, Villa A, Longhi R, Kaech SM, Fröhli E, Hajnal A, Kim SK, Pietrini G (1999). "PDZ-mediated interactions retain the epithelial GABA transporter on the basolateral surface of polarized epithelial cells". EMBO J. 18 (9): 2384–93. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.9.2384. PMC 1171321. PMID 10228153.
- Kamberov E, Makarova O, Roh M, Liu A, Karnak D, Straight S, Margolis B (2000). "Molecular cloning and characterization of Pals, proteins associated with mLin-7". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (15): 11425–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.15.11425. PMID 10753959.
- Tseng TC, Marfatia SM, Bryant PJ, Pack S, Zhuang Z, O'Brien JE, Lin L, Hanada T, Chishti AH (2001). "VAM-1: a new member of the MAGUK family binds to human Veli-1 through a conserved domain". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1518 (3): 249–59. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(01)00191-9. PMID 11311936.
- Harris BZ, Venkatasubrahmanyam S, Lim WA (2002). "Coordinated folding and association of the LIN-2, -7 (L27) domain. An obligate heterodimerization involved in assembly of signaling and cell polarity complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (38): 34902–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205856200. PMID 12110687.
- Hori K, Konno D, Maruoka H, Sobue K (2003). "MALS is a binding partner of IRSp53 at cell-cell contacts". FEBS Lett. 554 (1–2): 30–4. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01074-3. PMID 14596909.
- Leonoudakis D, Conti LR, Radeke CM, McGuire LM, Vandenberg CA (2004). "A multiprotein trafficking complex composed of SAP97, CASK, Veli, and Mint1 is associated with inward rectifier Kir2 potassium channels". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (18): 19051–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400284200. PMID 14960569.
- Leonoudakis D, Conti LR, Anderson S, Radeke CM, McGuire LM, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Yates JR, Vandenberg CA (2004). "Protein trafficking and anchoring complexes revealed by proteomic analysis of inward rectifier potassium channel (Kir2.x)-associated proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (21): 22331–46. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400285200. PMID 15024025.
- Olsen O, Wade JB, Morin N, Bredt DS, Welling PA (2005). "Differential localization of mammalian Lin-7 (MALS/Veli) PDZ proteins in the kidney". Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 288 (2): F345–52. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00235.2004. PMID 15494546.
- Dode L, Andersen JP, Raeymaekers L, Missiaen L, Vilsen B, Wuytack F (2006). "Functional comparison between secretory pathway Ca2+/Mn2+-ATPase (SPCA) 1 and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) 1 isoforms by steady-state and transient kinetic analyses". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (47): 39124–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506181200. PMID 16192278.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.