Homoserine
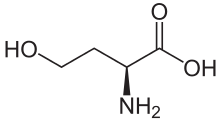
Homoserine (also called isothreonine) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2CH2OH. l-Homoserine is not one of the common amino acids encoded by DNA. It differs from the proteinogenic amino acid serine by insertion of an additional -CH2- unit into the backbone. Homoserine, or its lactone form, is the product of a cyanogen bromide cleavage of a peptide by degradation of methionine.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(S)-2-Amino-4-hydroxybutanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.538 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 119.12 g/mol |
| Melting point | 203 °C (decomposes) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Homoserine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of three essential amino acids: methionine, threonine (an isomer of homoserine), and isoleucine. It forms by two reductions of aspartic acid via the intermediacy of aspartate semialdehyde.[1]
References
- Berg, J. M.; Stryer, L. et al. (2002), Biochemistry. W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4684-0
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.