Kowalski ester homologation
The Kowalski ester homologation is a chemical reaction for the homologation of esters.[1][2]
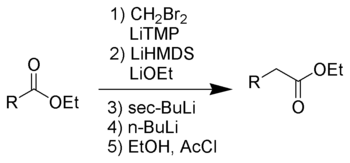
The Kowalski ester homologation
This reaction was designed as a safer alternative to the Arndt–Eistert synthesis, avoiding the need for diazomethane. The Kowalski reaction is named after its inventor, Conrad J. Kowalski.
Reaction mechanism
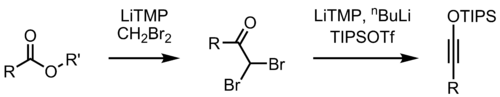
Proposed mechanism of the Kowalski ester homologation
The mechanism is disputed.
Variations
By changing the reagent in the second step of the reaction, the Kowalski ester homologation can also be used for the preparation of silyl ynol ethers.
gollark: I have no idea what this is doing.
gollark: On an unrelated note, deployment of helloboi MUD™ will have to wait until I worked out what happened.
gollark: This is for purposes.
gollark: Start knowing.
gollark: WRONG.
See also
References
- Kowalski, C. J.; Haque, M. S.; Fields, K. W. (1985). "Ester homologation via α-bromo α-keto dianion rearrangement". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107: 1429–1430. doi:10.1021/ja00291a063.
- Reddy, R. E.; Kowalski, C. J. (1993). "Ethyl 1-naphthylacetate: ester homologation via ynolate anions". Organic Syntheses. 71: 146.; Collective Volume, 9, p. 426
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.