Kieler Förde
Kieler Förde is an approximately 17 km (11 mi) long inlet of the Baltic Sea on the eastern side of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Formed by glacial movement during the last Ice Age, it divides Danish Wold peninsula from Wagria. Like the other inlets of förde-type, geologically it is not a fjord. It originates at the Hörn in centre-city Kiel and merges into the Bay of Kiel.
Kiel Fjord = Kiel harbor = Kieler Hafen; viewed from South towards the Baltic Sea in the northern background (2009)
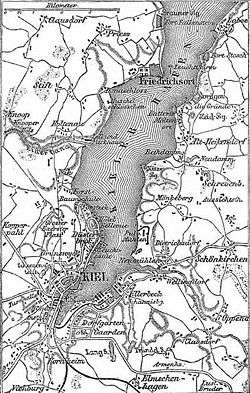
Historical map of the vicinity of Kiel, ca. 1888.
Kiel Fjord between Laboe and Mole Stickenhörn (nautical chart)

Aerial photograph, view from the Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft shipyard (front) towards Baltic Sea and the Laboe Naval Memorial (top right) in the north (2003)
The eastern terminus of the Kiel Canal is located along Kiel Förde leading into the Port of Kiel. At its narrowest point, the "Friedrichsorter Enge", the fjord is only one kilometre wide. The Schwentine enters Kieler Förde near Kiel-Dietrichsdorf.
Locations
Locations along the Kieler Förde:
Western shore
From north to south:
- Bülk (Bülk Lighthouse)
- Strande (fishery and sporting harbor)
- Kiel-Schilksee (Olympic harbor)
- Falckenstein (Kiel's duty-free beach)
- Kiel-Friedrichsort (traditionsreicher Industriestandort)
- Kiel-Holtenau (Kiel Canal)
- Kiel-Wik
- Kiel-Düsternbrook
- Kiel-Zentrum (offices of the large Scandinavian cruise ships)
Eastern shore
From south to north:
- Kiel-Gaarden (Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft,HDW)
- Kiel-Ellerbek (former fishing village, now Arsenal)
- Kiel-Wellingdorf (southern mouth of the Schwentine)
- Neumühlen-Dietrichsdorf (trade harbour "Ostuferhafen")
- Mönkeberg
- Kitzeberg
- Heikendorf
- Möltenort (fishery and sport harbour)
- Laboe (vacation site, Laboe Naval Memorial, U-Boat, fishery, and two sport harbours)
- Stein in Probstei
- Wendtorf in Probstei (vacation site, large natural yacht harbor (Marina Wendtorf), fishing village)
- Heidkate
gollark: Yes, I am.
gollark: However, it is already too late.
gollark: I see!
gollark: ↑
gollark: Or use Macron versioning, where you change it at random.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.