Kenneth B. Wiberg
Kenneth Berle Wiberg (born September 22, 1927) is an American Professor Emeritus of organic chemistry at Yale University. He contributed to many aspects of organic chemistry including physical and synthetic aspects.[1][2]
Scholarship
In the area of synthetic organic chemistry, Wiberg and his students reported the preparation of highly strained organic compounds bicyclobutane[3] and [1.1.1]propellane:[4]
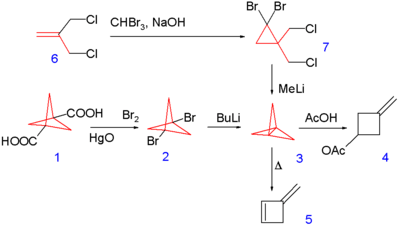 Scheme 1. Synthesis of [1.1.1]propellane
Scheme 1. Synthesis of [1.1.1]propellane
Recognition
- He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and an American Association of Arts and Sciences fellow.[5]
- In 1988, he won the Arthur C. Cope Award.[6]
- Asteroid 27267 Wiberg, discovered by American astronomer John V. McClusky at Fair Oaks Ranch Observatory (725) in 1999, was named in his honor.[2] The official naming citation was published by the Minor Planet Center on 7 January 2004 (M.P.C. 50464).[7]
gollark: e is the only nonzero value of a such that d/dx (a^x) = a^x.
gollark: Euler's constant.
gollark: e.
gollark: e is a slightly less appreciated constant.
gollark: You know what you should also do? Learn e.
References
- Kenneth B. Wiberg (1960). Laboratory Technique in Organic Chemistry. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0070700958.
- "27267 Wiberg (1999 YH7)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved June 12, 2020.
- Wiberg, K. B.; Lampman, G. M.; Ciula, R. P.; Connor, D. S.; Schertler, P.; Lavanish, J. (1965). "Bicyclo[1.1.0]butane". Tetrahedron. 21 (10): 2749–2769. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)98361-9.
- Wiberg, K. B.; Walker, F. H. (1982). "[1.1.1]Propellane". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104 (19): 5239–5240. doi:10.1021/ja00383a046.
- "Kenneth B. Wiberg, Faculty". Yale University Department of Chemistry.
- "Arthur C. Cope Award". American Chemical Society.
- "MPC/MPO/MPS Archive". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved June 12, 2020.
External links
- Homepage at Yale
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.