KLKB1
Plasma kallikrein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLKB1 gene.[5][6]
Function
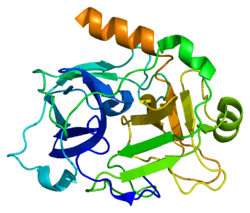
Plasma prekallikrein is a glycoprotein that participates in the surface-dependent activation of blood coagulation, fibrinolysis, kinin generation and inflammation. It is synthesized in the liver and secreted into the blood as a single polypeptide chain. Plasma prekallikrein is converted to plasma kallikrein by factor XIIa by the cleavage of an internal Arg-Ile bond. Plasma kallikrein therefore is composed of a heavy chain and a light chain held together by a disulfide bond. The heavy chain originates from the amino-terminal end of the zymogen and contains 4 tandem repeats of 90 or 91 amino acids. Each repeat harbors a novel structure called the apple domain. The heavy chain is required for the surface-dependent pro-coagulant activity of plasma kallikrein. The light chain contains the active site or catalytic domain of the enzyme and is homologous to the trypsin family of serine proteases. Plasma prekallikrein deficiency causes a prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time in patients.[7]
Interactions
KLKB1 has been shown to interact with High-molecular-weight kininogen.[8][9][10][11]
See also
- Kallikrein, a group of enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000164344 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000109764 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Yu H, Bowden DW, Spray BJ, Rich SS, Freedman BI (April 1998). "Identification of human plasma kallikrein gene polymorphisms and evaluation of their role in end-stage renal disease". Hypertension. 31 (4): 906–11. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.31.4.906. PMID 9535413.
- Chung DW, Fujikawa K, McMullen BA, Davie EW (August 1986). "Human plasma prekallikrein, a zymogen to a serine protease that contains four tandem repeats". Biochemistry. 25 (9): 2410–7. doi:10.1021/bi00357a017. PMID 3521732.
- "Entrez Gene: KLKB1 kallikrein B, plasma (Fletcher factor) 1".
- Thompson RE, Mandle R, Kaplan AP (October 1979). "Studies of binding of prekallikrein and Factor XI to high molecular weight kininogen and its light chain". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76 (10): 4862–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.10.4862. PMC 413037. PMID 291905.
- Page JD, You JL, Harris RB, Colman RW (October 1994). "Localization of the binding site on plasma kallikrein for high-molecular-weight kininogen to both apple 1 and apple 4 domains of the heavy chain". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 314 (1): 159–64. doi:10.1006/abbi.1994.1424. PMID 7944388.
- Herwald H, Jahnen-Dechent W, Alla SA, Hock J, Bouma BN, Müller-Esterl W (July 1993). "Mapping of the high molecular weight kininogen binding site of prekallikrein. Evidence for a discontinuous epitope formed by distinct segments of the prekallikrein heavy chain". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (19): 14527–35. PMID 7686159.
- Renné T, Dedio J, Meijers JC, Chung D, Müller-Esterl W (September 1999). "Mapping of the discontinuous H-kininogen binding site of plasma prekallikrein. Evidence for a critical role of apple domain-2". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (36): 25777–84. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.36.25777. PMID 10464316.
Further reading
- Thompson RE, Mandle R, Kaplan AP (1980). "Studies of binding of prekallikrein and Factor XI to high molecular weight kininogen and its light chain". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76 (10): 4862–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.10.4862. PMC 413037. PMID 291905.
- Aznar JA, España F, Aznar J, Tascon A, Jimenez C (1978). "Fletcher factor deficiency: report of a new family". Scandinavian Journal of Haematology. 21 (2): 94–8. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0609.1978.tb02498.x. PMID 694428.
- Henderson LM, Figueroa CD, Muller-Esterl W, Stain A, Bhoola KD (1993). Immunovisualisation of plasma prekallikrein and H-kininogen on human neutrophils and in human hepatocytes. Agents Actions Suppl. 38. pp. 590–4. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-7321-5_72. ISBN 978-3-0348-7323-9. PMID 1466300.
- Beaubien G, Rosinski-Chupin I, Mattei MG, Mbikay M, Chrétien M, Seidah NG (1991). "Gene structure and chromosomal localization of plasma kallikrein". Biochemistry. 30 (6): 1628–35. doi:10.1021/bi00220a027. PMID 1993180.
- McMullen BA, Fujikawa K, Davie EW (1991). "Location of the disulfide bonds in human plasma prekallikrein: the presence of four novel apple domains in the amino-terminal portion of the molecule". Biochemistry. 30 (8): 2050–6. doi:10.1021/bi00222a007. PMID 1998666.
- España F, Berrettini M, Griffin JH (1989). "Purification and characterization of plasma protein C inhibitor". Thromb. Res. 55 (3): 369–84. doi:10.1016/0049-3848(89)90069-8. PMID 2551064.
- Fujikawa K, Chung DW, Hendrickson LE, Davie EW (1986). "Amino acid sequence of human factor XI, a blood coagulation factor with four tandem repeats that are highly homologous with plasma prekallikrein". Biochemistry. 25 (9): 2417–24. doi:10.1021/bi00357a018. PMID 3636155.
- Herwald H, Jahnen-Dechent W, Alla SA, Hock J, Bouma BN, Müller-Esterl W (1993). "Mapping of the high molecular weight kininogen binding site of prekallikrein. Evidence for a discontinuous epitope formed by distinct segments of the prekallikrein heavy chain". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (19): 14527–35. PMID 7686159.
- Page JD, You JL, Harris RB, Colman RW (1994). "Localization of the binding site on plasma kallikrein for high-molecular-weight kininogen to both apple 1 and apple 4 domains of the heavy chain". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 314 (1): 159–64. doi:10.1006/abbi.1994.1424. PMID 7944388.
- Henderson LM, Figueroa CD, Müller-Esterl W, Bhoola KD (1994). "Assembly of contact-phase factors on the surface of the human neutrophil membrane". Blood. 84 (2): 474–82. PMID 8025275.
- Shimomura T, Kondo J, Ochiai M, Naka D, Miyazawa K, Morimoto Y, Kitamura N (1993). "Activation of the zymogen of hepatocyte growth factor activator by thrombin". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (30): 22927–32. PMID 8226803.
- Ciechanowicz A, Bader M, Wagner J, Ganten D (1994). "Extra-hepatic transcription of plasma prekallikrein gene in human and rat tissues". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197 (3): 1370–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1993.2628. PMID 8280154.
- Petersen LC, Sprecher CA, Foster DC, Blumberg H, Hamamoto T, Kisiel W (1996). "Inhibitory properties of a novel human Kunitz-type protease inhibitor homologous to tissue factor pathway inhibitor". Biochemistry. 35 (1): 266–72. doi:10.1021/bi951501d. PMID 8555184.
- Hermann A, Buchinger P, Somlev B, Rehbock J (1996). "High and low molecular weight kininogen and plasma prekallikrein/plasma kallikrein in villous capillaries of human term placenta". Placenta. 17 (4): 223–30. doi:10.1016/S0143-4004(96)90042-9. PMID 8761966.
- Durham SK, Suwanichkul A, Hayes JD, Herington AC, Powell DR, Campbell PG (1999). "The heparin binding domain of insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 increases susceptibility of IGFBP-3 to proteolysis". Horm. Metab. Res. 31 (2–3): 216–25. doi:10.1055/s-2007-978722. PMID 10226805.
- Renné T, Dedio J, Meijers JC, Chung D, Müller-Esterl W (1999). "Mapping of the discontinuous H-kininogen binding site of plasma prekallikrein. Evidence for a critical role of apple domain-2". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (36): 25777–84. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.36.25777. PMID 10464316.
- Hermann A, Arnhold M, Kresse H, Neth P, Fink E (1999). "Expression of plasma prekallikrein mRNA in human nonhepatic tissues and cell lineages suggests special local functions of the enzyme". Biol. Chem. 380 (9): 1097–102. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.657.2854. doi:10.1515/BC.1999.136. PMID 10543447.
- Cerf M, Raidoo D, Fink E, Fritz H, Bhoola K (2000). "Plasma kallikrein localisation in human blood vessels". Immunopharmacology. 44 (1–2): 75–80. doi:10.1016/S0162-3109(99)00112-5. PMID 10604527.