Jordan's inequality
In mathematics, Jordan's inequality, named after Camille Jordan, states that[1]
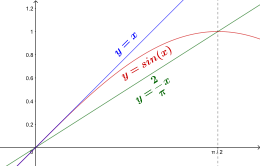
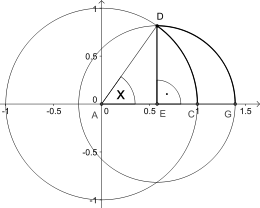
It can be proven through the geometry of circles (see drawing).[2]
Notes
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Jordan's inequality". MathWorld.
- Nach Feng Yuefeng, Proof without words: Jordan`s inequality, Mathematics Magazine, volume 69, no. 2, 1996, p. 126
Further reading
- Serge Colombo: Holomorphic Functions of One Variable. Taylor & Francis 1983, ISBN 0677059507, p. 167-168 (online copy)
- Da-Wei Niu, Jian Cao, Feng Qi: Generealizations of Jordan's Inequality and Concerned Relations. U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Volume 72, Issue 3, 2010, ISSN 1223-7027
- Feng Qi: Jordan's Inequality: Refinements, Generealizations, Applications and related Problems. RGMIA Res Rep Coll (2006), Volume: 9, Issue: 3, Pages: 243–259
- Meng-Kuang Kuo: Refinements of Jordan's inequality. Journal of Inequalities and Applications 2011, 2011:130, doi:10.1186/1029-242X-2011-130
gollark: I think mine is in some generic cheap Corsair cuboid.
gollark: I... still don't actually have much of a preference.
gollark: I see. Well, I have basically no opinion on this.
gollark: What are the pros and cons of each?
gollark: Oh, did you experience an orbital bee strike?
External links
- Jordan's inequality at the Proof Wiki
- Jordan's and Kober's inequalities at cut-the-knot.org
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Jordan's inequality". MathWorld.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.