John D'Alton (engineer)
John R D'Alton, born 1829, died 1904, was an engineer who migrated to Australia from Tipperary, Ireland in 1861 following his brother, William (1833–1907) who migrated in 1855. He worked as a mining surveyor at Ararat, Victoria before moving to Stawell, Victoria. He was the Borough engineer as well as the town valuer, surveyor and designer of several buildings, including the town hall built in 1870.[2]
John R D'Alton | |
|---|---|
 D'Alton before 1946[1] | |
| Born | 1829 Ireland |
| Died | 1904 |
| Occupation | Engineer |
| Known for | Borough Engineer Stawell, Victoria, Australia |
Notable work | The Stawell water supply system |
The Stawell water supply
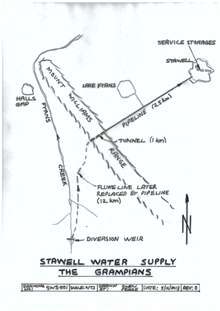
After gold was discovered around 1853, Stawell’s population began to grow and in 1866 residents realised they needed a permanent water supply. One of the schemes proposed was to block off the ends of the valley and flood the whole of Hall’s Gap. D’Alton came up with a more viable plan that is still in use.
The survey of the scheme was commenced in October 1873 but it was not until February 1875 that the first sod of the tunnel was turned by the then Mayor, Mr HC Purcell.[3]
His proposal was to bore a tunnel through the Mt William range, a distance of 1 km, and have the water diverted from Fyan’s Creek by open channels and flumes. It commenced operation in December 1881.
The system worked by gravity and delivered up to 38 megalitres a day to the Big Hill reservoir in Stawell. Much of Stawell’s water supply still comes from Fyan’s Creek and parts of the original system are still in use, including the tunnel. A new weir has been built near the original and in 1978 a chlorination plant was added. The original brick-lined reservoir which held a maximum of 11 megalitres has had additional reservoirs added and total capacity is now 500 megalitres.
The original 12 km flume, on timber structures and using inverted syphons or aqueducts to cross gullies, was replaced with by steel initially but was replaced by underground piping in 1955. The construction of the 1 km long tunnel was started from both ends in 1875 and, for the first time in Victoria, dynamite was used. It was safer and more effective than black powder (gunpowder). Using a compressed air drilling machine, the two sides met, after many delays, with precision five years later.[1]
The original cost was estimated at £84.500. The Borough Council applied for a loan for that amount on September 10, 1874 and in October the Government advanced a loan of £10000. The project started 18 February 1875. A full holiday was declared and a picnic held at the eastern end of the proposed tunnel. A marquee that seated 250 was erected and hot meals were served there in five relays. The scheme was completed in December 1881 at a cost of £115583.[4]
The Halls Gap and Grampians Historical Society list the materials used in the system as:
“7 miles (11 km) of fluming, containing approximately 5000 sleepers and frames, 30 expansion joints, 3 large siphons, 4 aqueducts, 3300 feet (1000 m) of tunnel and 15 miles (24 km) of 12 inch (30 cm) diameter mains containing 8 valves, 17 scour valves and 24 air valves. The mains line also consisted of 9500 lead joints with a total weight of 54 tons of lead and 5 tons of yarn. Twenty miles (30 km) of reticulation pipes were also needed with 850 services connected to the mains.” [5]
Family
John’s father, William (1791–1863), had managed an estate for Lord Ormond in Ireland. He married his cousin Henrietta Hayden (1801–1886)
John married Jane Galbraith (1834–1873) just as they left for Australia. Jane gave birth to eight children but died the day after the last was born.
D’Alton sent an urgent message to his family in Ireland asking for someone to come out and help. His widower mother, Henrietta, did not want to part with her family so they sold up and all migrated in 1875. The family was not small, there was Henrietta, brothers Charles, St Eloy and William (who had been in New Zealand) and sisters Susan, twins, Sophia and Henrietta, as well as the family governess, Miss Carpenter.[6]
By the time they arrived John had remarried a widow Catherine Denholm-Fulton who already had five children. They were to add a further three.
Henrietta settled in Halls Gap and the rest of the family in the Mt Arapiles area. During this time he undertook the surveying for the water supply.[2]
References
- Engineering Heritage Marker dedicated 12 October 2014: Engineers Australia, Parks Victoria, Engineers Australia, GWM Water, Northern Grampians Shire Council, IPWEA Victoria
- Bridging the Gap: the History of Hall's Gap from 1840, Ida Stanton, Publisher: I. Stanton 1988, ISBN 0731633075
- Pomonal: A Picturesque Place Revisited, Isabel Armer, Publisher: Pomonal Progress Association 2013, ISBN 9780646592909
- Shepherd’s Gold: the story of Stawell, C E Sayers, page 141, Publisher: Melbourne: Cheshire 1966
- Victoria's Wonderland: A Grampians History, Compiled by The Halls Gap and Grampians Historical Society 2006 page 37
- Good Country for a Grant: A History of the Stawell Shire, Robert Kingston