Insult (legal)
Insult is the infringement of another human's honor by whatsoever means of expression,[1][2] in particular an offensive statement or gesture communicated, and is a crime in some countries.[3][4] The distinction between insult and defamation is that, from a focussing point of view, the former ascribes a value whereas the latter attributes or imputes a fact.[5]
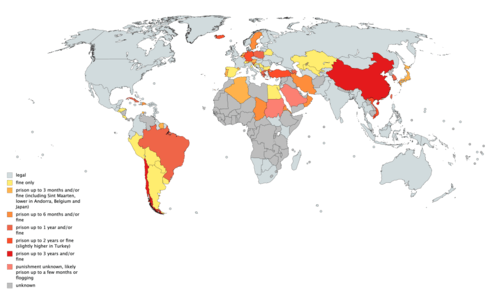
Law by jurisdiction
Africa
Algeria
Insult (Arabic: سَبَّة, "sabba", French: injure) is punishable by prison up to three months or a fine from 10,000 DZD (ca. $78.50) to 25,000 DZD (ca. $196) or both.[6]
Chad
Public insult (injure) not through press is punishable by prison up to six months or a fine from 25,000 XAF (ca. $41) to 50,000 XAF (ca. $82.50) or both.[7]
Egypt
Public insult (سَبَّة, "sabba") is punishable by a fine from 2,000 EGP (ca. $126) to 10,000 EGP (ca. $633).[8] If the insult is published in a newspaper or elsewhere, the penalty is a fine from 4,000 EGP (ca. $253) to 20,000 EGP (ca. $1,266).[9]
Eritrea
Insult is punishable by prison up to one month or by a fine from 1 ERN (ca. $0.06) to 1,000 ERN (ca. $66.50).[10] If the insult is grossly obscene, refers to the profession or is otherwise severe, the penalty is prison up to six months or a fine from 5,001 ERN (ca. $333) to 20,000 ERN (ca. $1,333).[11]
Asia
Azerbaijan
Public insult (təhqir) is punishable either by prison up to six months, a fine from 1,000 AZN (ca. $588) to 1,500 AZN (ca. $882), income subtraction from 5% to 20% for up to one year or public work from 60 to 120 days.[12] If the insult is committed with a pseudonymous profile or account in the Internet, the penalty is either prison up to one year, a fine from 1,000 AZN to 2,000 AZN (ca. $1,176), income subtraction from 5% to 20% for up to two years or public work from 90 to 120 days.[13]
China
Serious insult (侮辱, "wǔrǔ") by assault or other means is punishable by prison up to three years or surveillance up to two years.[14] If the insult by assault is too serious, it may be subsidiary to violent crimes instead. In Macau, insult (Chinese: 侮辱, "wǔrǔ", Portuguese: injúria) is punishable by prison up to three months or by a fine up to 120 daily units.[15]
Iran
Satirization is punishable by prison up to six months.[16]
Japan
Public insult (侮辱, "bujoku") is punishable by prison up to one month or by a fine from ¥1,000 (ca. $9) to ¥10,000 (ca. $92).[17]
Kazakhstan
Insult (қорлау, "qorlay'") is punishable by a fine of up to 100 monthly calculation indices.[18] If the insult is committed in public, by mass media or telecommunication networks, the penalty is a fine of up to 200 monthly calculation indices.[19]
Oman
Insult is punishable by prison up to three months, a fine from 100 OMR (ca. $259) to 300 OMR (ca. $777) or both.[20] If the insult is committed in public, the penalty is prison up to six months, a fine from 200 OMR to 500 OMR (ca. $1,295) or both.[21]
South Korea
Public insult (모욕, "moyok") is punishable by prison up to one year or by a fine up to ₩2 million (ca. $1,600).[22]
Taiwan
Public insult (侮辱, "wǔrǔ") is punishable by prison up to two months or by a fine up to 9,000 TWD (ca. $297).[23] If the insult is committed by assault, the penalty is prison up to one year or a fine up to 15,000 TWD (ca. $495).[24]
Turkey
Insult (hakaret) is punishable by prison up to two years or by fine.[25] If the insult is committed in public, the penalty is prison up to 2,33 years or a fine increased by up to a sixth.[26]
Uzbekistan
Only the second insult (haqorat qilish) after an administrative measure is punishable either by a fine up to 200 basic calculation units, income subtraction from 10% to 30% for up to one year or up to 60 days of public work.[27] If the insult is printed or otherwise reproduced, the penalty is either a fine from 200 to 400 basic calculation units, income subtraction from 10% to 30% for one to two years or public work from 60 to 75 days.[28]
Vietnam
Serious insult (làm nhục) is punishable by a fine from 10,000,000 VND (ca. $421) to 30,000,000 VND (ca. $1,265) or community service up to three years, which means public work and partial income subtraction.[29] For insult against someone who teaches, nurtures, cares for or cures the offender and for insult by means of a computer network, telecommunication network or electronic device, the penalty is prison up to two years.[30]
Europe
Albania
Insult (fyerje) is punishable by a fine of 40,000 ALL (ca. $350) to 1 million ALL (ca. $8,350).[31] If the insult is committed in public, the penalty is a fine from 40,000 ALL to 3 million ALL (ca. $25,100).[32]
Andorra
Grave or public insult (injúria) is punishable by prison up to 12 days.[33]
Austria
Insult (Beleidigung) or derision (Verspottung) in public or in front of multiple people is punishable by prison up to three months or by a fine up to 180 daily units.[34]
Belarus
Insult (оскорбление, "oskorblenie") in public, in a public work or telecommunication network is punishable by fine or restriction of liberty up to three years.[35]
Belgium
Insult (injure) is punishable by prison up to two months or by a fine from €26 (ca. $28) to €500 (ca. $540).[36]
Bulgaria
Insult is punishable by a fine from 1,000 BGN (ca. $550) to 3,000 BGN (ca. $1,675).[37] If the insult is committed in public, divulged through print or some other way, the penalty is a fine from 3,000 BGN to 10,000 BGN (ca. $5,570).[38]
Croatia
Insult (uvreda) is punishable by a fine up to 90 daily units.[39] If the insult is committed through press, radio, television, a public computer system or network, at a public gathering or otherwise made publicly accessible, the penalty is a fine up to 180 daily units.[40]
Germany
Insult (Beleidigung) is punishable by prison up to one year or by fine.[41] If the insult is committed by assault, the penalty is prison up to two years or a fine.[42]
Greece
Insult (εξύβριση) is punishable by prison up to six months or by fine.[43] If the insult is committed in public, the penalty is prison up to one year or a fine.[44]
Iceland
Insult (móðgun) is punishable by prison up to one year or by fine.[45] For insult against one's spouse, ex-spouse, child or close relative, the penalty is prison up to two years.[46] Upbraiding (brigsl) without a reason is punishable by a fine.[47]
Liechtenstein
Insult (Beleidigung) or derision (Verspottung) in front of someone else is punishable by prison up to one month or by a fine up to 60 daily units.[48] If the insult occurs in public or in front of multiple people, the penalty is prison up to three months or a fine up to 180 daily units.[49]
Netherlands
Insult (belediging) not protecting public goods intentiously is punishable by prison up to three months or a fine up to €4,350 (ca. $4,739).[50] In Sint Maarten, insult is punishable by prison up to three months or by a fine up to $250.[51] In Aruba, it is punishable by prison up to three months or by a fine up to 300 AWG (ca. $165).[52]
Poland
Insult (zniewaga) is punishable by fine or restriction of liberty.[53] If the insult is committed by mass media, the penalty is either prison up to one year, a fine or restriction of liberty.[54]
Portugal
Insult (injúria) is punishable by prison up to three months or by a fine up to 120 daily units.[55]
San Marino
Insult (ingiuria) in front of multiple people is punishable by a fine of 10 to 40 daily units.[56]
Serbia
Insult (uvreda) is punishable by a fine from 20 to 100 daily units or from 40,000 RSD (ca. $367) to 200,000 RSD (ca. $1,835).[57] If the insult is committed through the press, radio, television, other media or at a public gathering, the penalty is a fine from 80 to 240 daily units or from 150,000 RSD (ca. $1,376) to 450,000 RSD (ca. $4,130).[58]
Slovenia
Insult (razžalitev) that, not contemptuously intended, does not pertain to a scientific, literary or artistic work, serious criticism, official duty, social or political activity, defense of a right or protection of justified benefits is punishable by prison up to three months or by fine.[59] If the insult is committed through press, radio, television, on a website or through other media, the penalty is prison up to six months or a fine.[60]
Spain
Insult (injuria) of generally grave nature, with these effects or circumstances is punishable by a fine of 3 to 7 monthly units.[61] If such insult is committed in public, the penalty is a fine from 6 to 14 monthly units.[62]
Sweden
Insult (förölämpning) is punishable by fine.[63] If the insult is gross, the penalty is prison up to six months or a fine.[64]
Switzerland
Insult (German: Beschimpfung, French: injure, Italian: ingiuria, Romansh: ingiuria) is punishable by a fine up to 90 daily units.[65]
North America and the Caribes
Costa Rica
Insult (injuria) is punishable by a fine from 10 to 50 daily units.[66] If the insult is committed in public, the penalty is a fine from 15 to 75 daily units.[67]
Cuba
Insult (injuria) is punishable by prison up to one year or by a fine from 100 to 300 units.[68]
Dominican Republic
Public insult (injuria) is punishable by prison up to six months and by fine.[69]
El Salvador
Insult (injuria) is punishable by a fine from 50 to 100 daily units.[70] If the insult is committed in public, the penalty is a fine from 100 to 180 daily units.[71]
Honduras
Insult (injuria) of generally grave nature, with these effects or circumstances is punishable by a fine from 100 to 200 daily units.[72] If such insult is committed in public, the penalty is a fine from 200 to 500 daily units.[73]
South America
Argentina
Insult (injuria) not referring to or protecting public goods is punishable by a fine of 1,500 ARS (ca. $23) to 20,000 ARS (ca. $309).[74]
Bolivia
Insult (injuria) by means of mass diffusion is punishable by a fine from 100 to 250 daily units.[75]
Brazil
Insult (injúria) is punishable by prison up to six months or by fine.[76] If the insult is committed by assault or is demeaning by its nature or means, the penalty is prison up to one year and a fine.[77]
Chile
Insult (injuria) is punishable by prison up to two months or by fine.[78] Written and public insults are punishable by prison up to 1,48 years and by a fine from 6 to 10 monthly units.[79] Written and public insults of general affronting nature, occasion or circumstances and written and public insults grave due to the state, dignity and circumstances of the offended one and the offender are punishable by prison up to three years and by a fine from 11 to 20 monthly units.[80]
Paraguay
Insult (injuria) is punishable by a fine up to 90 daily units.[81] If the insult is committed in front of someone else, the penalty is a fine up to 180 daily units.[82]
Peru
Insult (injuria) is punishable by a fine from 60 up to 90 daily units or by public work from 10 to 40 days.[83]
Suriname
Insult (belediging) not protecting public goods intentiously is punishable by prison up to three months, a fine up to 10,000 SRD (ca. $1,329) or both.[84]
Uruguay
Insult (injuria) is punishable by a fine from 60 UR (ca. $1,700) to 400 UR (ca. $11,450).[85] If the insult is committed in public or divulged publicly, the penalty is a fine from 70 UR (ca. $2,000) to 533,33 UR (ca. $15,250).[86]
References
- de Pablo Serrano, Alejandro (2014), Los delitos contra el honor en el derecho penal español y en el derecho comparado, Vallodid: Vallodid University, p. 349
- Mijatović, Dunja (2017), Defamation and Insult Laws in the OSCE Region, Organization for Cooperation and Security Europe, p. 9
- Mijatović, Dunja (2017), Defamation and Insult Laws in the OSCE Region, Organization for Cooperation and Security Europe, p. 7
- Clooney, Amal; Webb, Philippa (2018), "The Right to Insult in International Law" in Columbia Human Rights Law Review, volume 48, number 2, p. 2
- Mijatović, Dunja (2017), Defamation and Insult Laws in the OSCE Region, Organization for Cooperation and Security Europe, p. 9
- Algerian Penal Code (2015), Art. 299 par. 1
- Chadian Penal Code (2017), Art. 364 par. 1
- Egyptian Penal Code (2019), Art. 306, 171
- Egyptian Penal Code (2019), Art. 307
- Eritrean Penal Code (2015), Art. 302 par. 2
- Eritrean Penal Code (2015), Art. 302 par. 1 b)-d)
- Azerbaijani Criminal Code (2019), Art. 148, 49 par. 2, 47 par. 2
- Azerbaijani Criminal Code (2019), Art. 148-1, 49 par. 2, 47 par. 2
- Chinese Criminal Code (2017), Art. 246, 38
- Macau Penal Code (2017), Art. 175
- Iranian Criminal Sharia (2013), Art. 700
- Japanese Penal Code (2019), Art. 231, 16, 17
- Kazakh Criminal Code (2018), Art. 131 par. 1
- Kazakh Criminal Code (2018), Art. 131 par. 2
- Omani Penal Code (2018), Art. 328
- Omani Penal Code (2018), Art. 327
- South Korean Criminal Code (2018), Art. 311
- Taiwanese Criminal Code (2020), Art. 309 par. 1
- Taiwanese Criminal Code (2020), Art. 309 par. 2
- Turkish Penal Code (2020), Art. 125 par. 1
- Turkish Penal Code (2020), Art. 125 par. 4
- Uzbek Criminal Code (2020), Art. 140 par. 1, 46 par. 1, 45 par. 2
- Uzbek Criminal Code (2020), Art. 140 par. 2, 46 par. 1, 45 par. 2
- Vietnamese Penal Code (2018), Art. 155 par. 1
- Vietnamese Penal Code (2018), Art. 155 par. 2, e), f)
- Albanian Penal Code (2017), Art. 119 par. 1
- Albanian Penal Code (2017), Art. 119 par. 2
- Andorran Penal Code (2020), Art. 174, 36 Nr. 2
- Austrian Criminal Code (2020), § 115 par. 1
- Belarussian Criminal Code (2019), Art. 189
- Belgian Penal Code (2019), Art. 448
- Bulgarian Criminal Code (2017), Art. 146 par. 1
- Bulgarian Criminal Code (2017), Art. 147 par. 1 nr. 1, 2
- Croatian Criminal Code (2020), Art. 147 par. 1
- Croatian Criminal Code (2020), Art. 147 par. 2
- German Criminal Code (2020), § 185 par. 1
- German Criminal Code (2020), § 185 par. 2
- Greek Penal Code (2019), Art. 361 par. 1
- Greek Penal Code (2019), Art. 361 par. 2
- Icelandic Criminal Code (2019), Art. 234
- Icelandic Criminal Code (2019), Art. 233b
- Icelandic Criminal Code (2019), Art. 237
- Liechtensteiner Criminal Code (2019), § 115 par. 1
- Liechtensteiner Criminal Code (2019), § 115 par. 2
- Dutch Criminal Code (2020), Art. 266, 23 par. 4 nr. 2
- St. Maartener Criminal Code (2015), Art. 278, 27 par. 4 nr. 1
- Aruban Criminal Code (2014), Art. 278
- Polish Criminal Code (2020), Art. 216 par. 1
- Polish Criminal Code (2020), Art. 216 par. 2
- Portuguese Penal Code (2020), Art. 181 par. 1, 85
- Sanmarinese Penal Code (2019), Art. 184, 85 par. 3 nr. 2
- Serbian Criminal Code (2019), Art. 170 par. 1
- Serbian Criminal Code (2019), Art. 170 par. 2
- Slovene Criminal Code (2017), Art. 158 par. 1, 3
- Slovene Criminal Code (2017), Art. 158 par. 2
- Spanish Penal Code (2020), Art. 208, 209
- Spanish Penal Code (2020), Art. 209
- Swedish Criminal Code (2020), Chapter 5, § 3 par. 1
- Swedish Criminal Code (2020), Chapter 5, § 3 par. 2
- Swiss Criminal Code (2020), Art. 177 par. 1
- Costa Rican Penal Code (2019), Art. 145 s. 1
- Costa Rican Penal Code (2019), Art. 145 s. 2
- Cuban Penal Code (2020), Art. 320
- Dominican Penal Code, Art. 309
- Salvadoran Penal Code (2020), Art. 179 par. 1
- Salvadoran Penal Code (2020), Art. 179 par. 2
- Honduran Penal Code (2019), Art. 229 par. 1, 3
- Honduran Penal Code (2019), Art. 229 par. 1, 3
- Argentinian Penal Code (2018), Art. 111
- Bolivian Penal Code (2017), Art. 309 par. 2
- Brazilian Penal Code (2019), Art. 140 par. 1
- Brazilian Penal Code (2019), Art. 140 par. 2
- Chilean Penal Code (2020), Art. 419 s. 2, 56
- Chilean Penal Code (2020), Art. 419 s. 1, 418 par. 2, 56
- Chilean Penal Code (2020), Art. 417 nr. 4, 5, Art. 418 par. 1, 56
- Paraguayan Penal Code, Art. 152 par. 1 nr. 2
- Paraguayan Penal Code, Art. 152 par. 2
- Peruvian Penal Code (2018), Art. 130
- Surinamese Criminal Code (2015), Art. 325, 40 par. 2 nr. 2
- Uruguayan Penal Code (2020), Art. 334
- Uruguayan Penal Code (2020), Art. 335