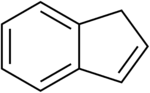
Indene
Indene is a flammable polycyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C9H8. It is composed of a benzene ring fused with a cyclopentene ring. This aromatic liquid is colorless although samples often are pale yellow. The principal industrial use of indene is in the production of indene/coumarone thermoplastic resins. Substituted indenes and their closely related indane derivatives are important structural motifs found in many natural products and biologically active molecules, such as sulindac.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-Indene | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Bicyclo[4.3.0]nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene | |
| Other names
Benzocyclopentadiene Indonaphthene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 635873 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.176 |
| 27265 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8 | |
| Molar mass | 116.16 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Density | 0.997 g/mL |
| Melting point | −1.8 °C (28.8 °F; 271.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 181.6 °C (358.9 °F; 454.8 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 20.1 (in DMSO)[2] |
| -80.89·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| Flash point | 78.3 °C (172.9 °F; 351.4 K) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 ppm (45 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Benzofuran, Benzothiophene, Indole |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Isolation
Indene occurs naturally in coal-tar fractions boiling around 175–185 °C. It can be obtained by heating this fraction with sodium to precipitate solid "sodio-indene." This step exploits indene's weak acidity evidenced by its deprotonation by sodium to give the indenyl derivative. The sodio-indene is converted back to indene by steam distillation.[4]
Reactivity
Indene readily polymerises. Oxidation of indene with acid dichromate yields homophthalic acid (o-carboxylphenylacetic acid). It condenses with diethyl oxalate in the presence of sodium ethoxide to form indene-oxalic ester, and with aldehydes or ketones in the presence of alkali to form benzofulvenes. The latter are highly coloured. Treatment of indene with organolithium reagents give lithium indenyl compounds:
- C9H8 + RLi → LiC9H7 + RH
Indenyl is a ligand in organometallic chemistry, giving rise to many transition metal indenyl complexes.[5]
References
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0340". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Bordwell FG (1988). "Equilibrium acidities in dimethyl sulfoxide solution". Accounts of Chemical Research. 21 (12): 456–463. doi:10.1021/ar00156a004. Bordwell pKa Table in DMSO Archived 2008-10-09 at the Wayback Machine
- Wu, Jie; Qiu, Guanyinsheng (2014). "Generation of Indene Derivatives by Tandem Reactions". Synlett. 25 (19): 2703–2713. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1379318.
- Gerd Collin, Rolf Mildenberg, Mechthild Zander, Hartmut Höke, William McKillip, Werner Freitag, Wolfgang Imöhl “Resins, Synthetic” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2000.
- O'Connor, Joseph M.; Casey, Charles P. (1987). "Ring-Slippage Chemistry of Transition Metal Cyclopentadienyl and Indenyl Complexes". Chemical Reviews. 87 (2): 307–318. doi:10.1021/cr00078a002.
External links
- W. v. Miller, Rohde (1890). "Zur Synthese von Indenderivaten". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 23 (2): 1881–1886. doi:10.1002/cber.18900230227.
- W. v. Miller, Rohde (1890). "Zur Synthese von Indenderivaten". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 23 (2): 1887–1902. doi:10.1002/cber.18900230228.
- Finar, I. L. (1985). Organic Chemistry. Longman Scientific & Technical. ISBN 0-582-44257-5.