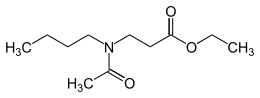
Ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate
Ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (trade name IR3535) is an insect repellent. As ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate is solely a repellent, it has no killing action and does not give rise to selection pressure or development of resistance.[1] It is a colorless and almost odorless oil and is intended to be applied to the skin of humans and animals.[1][2] It has a broad efficacy against various insects like mosquitoes, ticks, lice, and other bugs.[1][2][3] Ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate is safe for use on infants, pregnant and breastfeeding women. It is biodegradable and completely degraded in the environment within a very short time.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethyl N-acetyl-N-butyl-β-alaninate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.052.560 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H21NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 215.293 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Almost odorless |
| Density | 0.998 g/cm3 (at 20 °C) |
| 70 g/L (at 20 °C) | |
| Solubility in Acetone, ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, n-heptane, methanol, p-xylene | >250 g/L (at RT) |
| log P | 1.7 (at 23 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H319 |
| P280, P305+351+338, P337+313 | |
| Flash point | 159 °C (318 °F; 432 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chemistry
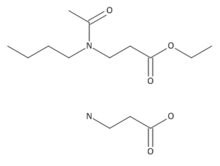
Ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate and beta-alanine
Ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate is a derivative of beta-alanine.[4]
gollark: Coral Shoe Transfer Protocol when?
gollark: Apiohypnoforms inbound.
gollark: As planned.
gollark: Are you ”””enjoying⅛⅛⅛⅛⅛ awesome?
gollark: Why use the Discord app when you could use W E B D I S C O R D by osmarks.tk™?
References
External links
- Barnard, Donald R.; Bernier, Ulrich R.; Posey, Kenneth H.; Xue, Rui-De (2002). "Repellency of IR3535, KBR3023,para-menthane-3,8-diol, and Deet to Black Salt Marsh Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Everglades National Park" (PDF). Journal of Medical Entomology. 39 (6): 895–899. doi:10.1603/0022-2585-39.6.895. PMID 12495189. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-21.
- Tick Bite Prevention & the Use of Insect Repellents
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.