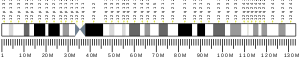
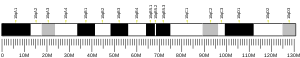
IKZF4
Zinc finger protein Eos is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IKZF4 gene.[5][6]
Members of the Ikaros (ZNFN1A1; MIM 603023) family of transcription factors, which includes Eos, are expressed in lymphocytes and are implicated in the control of lymphoid development.[supplied by OMIM][6]
Interactions
IKZF4 has been shown to interact with CTBP1[7] and IKZF1.[5][8]
gollark: It's temporarily offline.
gollark: Why? BEES™.
gollark: Time to RANDOMLY RECONFIGURE OSMARKS.TK AGAIN!
gollark: An AI designed to write optimized BF versions of itself will be far too confused by reality to wipe out humans.
gollark: We should make self-improving AIs in esolangs so that their internal models of things will be far enough from reality that they cannot destroy humanity.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000123411 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000002578 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Perdomo J, Holmes M, Chong B, Crossley M (Jan 2001). "Eos and pegasus, two members of the Ikaros family of proteins with distinct DNA binding activities". J Biol Chem. 275 (49): 38347–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005457200. PMID 10978333.
- "Entrez Gene: IKZF4 IKAROS family zinc finger 4 (Eos)".
- Perdomo, José; Crossley Merlin (Dec 2002). "The Ikaros family protein Eos associates with C-terminal-binding protein corepressors". Eur. J. Biochem. Germany. 269 (23): 5885–92. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03313.x. ISSN 0014-2956. PMID 12444977.
- Honma, Y; Kiyosawa H; Mori T; Oguri A; Nikaido T; Kanazawa K; Tojo M; Takeda J; Tanno Y; Yokoya S; Kawabata I; Ikeda H; Wanaka A (Mar 1999). "Eos: a novel member of the Ikaros gene family expressed predominantly in the developing nervous system". FEBS Lett. NETHERLANDS. 447 (1): 76–80. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00265-3. ISSN 0014-5793. PMID 10218586.
Further reading
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Bao J, Lin H, Ouyang Y, et al. (2005). "Activity-dependent transcription regulation of PSD-95 by neuregulin-1 and Eos". Nat. Neurosci. 7 (11): 1250–8. doi:10.1038/nn1342. PMID 15494726.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Perdomo J, Crossley M (2003). "The Ikaros family protein Eos associates with C-terminal-binding protein corepressors". Eur. J. Biochem. 269 (23): 5885–92. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03313.x. PMID 12444977.
- Koipally J, Georgopoulos K (2002). "A molecular dissection of the repression circuitry of Ikaros". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (31): 27697–705. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201694200. PMID 12015313.
- Nagase T, Nakayama M, Nakajima D, et al. (2001). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 8 (2): 85–95. doi:10.1093/dnares/8.2.85. PMID 11347906.
- Honma Y, Kiyosawa H, Mori T, et al. (1999). "Eos: a novel member of the Ikaros gene family expressed predominantly in the developing nervous system". FEBS Lett. 447 (1): 76–80. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00265-3. PMID 10218586.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.