Hyperaulax ridleyi
Hyperaulax ridleyi is a species of tropical air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Odontostomidae.[2]
| Hyperaulax ridleyi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Drawing of the apertural view of a shell of Hyperaulax ridleyi. | |
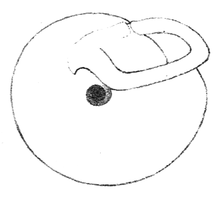 | |
| Drawing of the umibilical view of a shell of Hyperaulax ridleyi. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| (unranked): | clade Heterobranchia clade Euthyneura clade Panpulmonata clade Eupulmonata clade Stylommatophora informal group Sigmurethra |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | H. ridleyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Hyperaulax ridleyi (E. A. Smith, 1890)[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Bulimulus (Hyperaulax) ridleyi | |
Hyperaulax ridleyi is the type species of the genus Hyperaulax.[3]
This species is native to, and its occurrence is restricted to, Fernando de Noronha, an island off the coast of Brazil. The snail was described in 1890 by Edgar Albert Smith, a zoologist with the British Museum.[1] The type specimen is stored in the British Museum of Natural History.[4]
Shell description
The shell is umbilicated, ovate, conic above, moderately solid, brown with a buff line at the periphery, very delicately sculptured with lines of growth, and sometimes has low wrinkles and fine impressed spiral striae. The spire of the shell is conic. The apex is obtuse. The sculpture of the nepionic whorls (the whorls immediately following the embryonic whorls) has superficial vermiculate (worm-like) wrinkles. The shell has 5½ slightly convex whorls. The last whorl is a little descending and then slightly ascending in front, distinctly constricted behind the peristome. The base of the shell is perforated by a deep and conspicuous, though not wide, umbilicus.[3]
The shell aperture is ovate, and is a fleshy-brown color inside. There is a pale median line in half the length of the shell. The peristome is flatly reflexed throughout. The outer lip is subangularly arcuate above, terminations joined by a thin or thick parietal callus, which is thickened and somewhat tubercular above, separated by a vertical groove or channel from a similar callous lobe on the outer lip, near its insertion.[3]
The width of the shell is 6.2-7.2 mm. The height of the shell is 10.5-12.5 mm. The height of the aperture is 5.2-6.2 mm.[3] The width of the type specimen is 5.9. The height of the type specimen is 11.4.[4]
Habitat
It lives in trees and on the ground.[5]
Predators
References
This article incorporates public domain text from reference.[3]
- Ridley, Henry; Boulenger, George (31 July 1890). "Notes on the Zoology of Fernando Noronha". The Journal of the Linnean Society Zoology. London. 20: 483. Page 501. Plate 30. figure 9.
- Breure A. S. H. & Ablett J. D. (2012) "Annotated type catalogue of the Bothriembryontidae and Odontostomidae (Mollusca, Gastropoda, Orthalicoidea) in the Natural History Museum, London". ZooKeys 182: 1-70. doi:10.3897/zookeys.182.2720.
-

- Breure, A. S. H . & J. R. Schouten (27 February 1985). "Notes on and descriptions of Bulimulidae (Mollusca, Gastropoda), III." Zoologische Verhandelingen Leiden 216: 1-98, figs. 1-33, pls. 1-4. ISSN 0024-1652. PDF
- Hyperaulax ridleyi (Smith, 1890). CdB - Conchology. Accessed 22 December 2009
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hyperaulax ridleyi. |