Huy (hills)
The Huy (pronounced [hyː], from the Old High German for Höhe = "heights") or Huywald is a ridge, up to 314.8 metres high,[1] in western Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. It lies in the northern part of the district of Harz, about 10 kilometres northwest of Halberstadt and a few kilometres west of Schwanebeck. It is chiefly composed of bunter sandstone and muschelkalk and has been designated a protected area. Towards the north and northwest the terrain falls away into the Großes Bruch. Towards the east the Huy transitions to the Magdeburg Börde; to the south and southwest it is adjoined by the Harz Foreland and the Harz Mountains.
| Huy | |
|---|---|
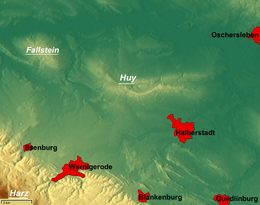 Overview map of the area with the Huy in the centre. Top left: the Fallstein
| |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Buchenberg |
| Elevation | 314 m (1,030 ft) |
| Coordinates | 51°57′18″N 10°58′23″E |
| Geography | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Saxony-Anhalt |
The highest hill, the 314-metre-high Buchenberg, is located about three kilometres southwest of Dingelstedt am Huy, within the municipality of Huy. The Huy Forest (Huywald) is one of the largest, almost pure beech forests of central Europe.
On the crest of the Huy lies the Benedictine abbey of Huysburg, which is on the Romanesque Road, and Daneil's Cave.
Politically the Huy belongs to the parish of the same name. Its villages lie around the ridge itself.
History
.jpg)
Between 1882 and 1887 several drillings were carried out in the Huy about five kilometres from Anderbeck. They uncovered large deposits of potash and rock salt not far below the surface. This led to the foundation of the Wilhelmshall Mining Company (Bergrechtliche Gewerkschaft Wilhelmshall), which started mining salts here in 1926 and triggered a boom in the Huy region. The Jerxheim–Dedeleben–Nienhagen railway, with its industrial siding built in 1891 from Anderbeck to the potash works, was constructed primarily for the transportation of potash salts.
In 1897 a cement works built close to Schwanebeck that used a limestone quarry in the Huy was also connected to the railway line.
During quarrying work in 1910 ice age kettles were discovered.
From 1934 the Dingelstedt b Halberstadt Army Ammunition Depot (Heeres-Munitionsanstalt Dingelstedt b Halberstadt) was located in the Huy in several old potash mine galleries. In 1944 up to 600 employees and forced labourers worked here. Two explosions on 21 September 1944 caused 59 deaths. From 1957 to 1961 there was discussion about reopening the potash mines, but the idea was eventually dropped. By 1962 the underground facilities were cleared and, in 1978, the shafts were flooded.
Today the Huy is heavily used by hikers, cyclists and riders.
Transport
The Huy lies in the angle formed by the B 244 federal road heading westwards from Helmstedt to Wernigerode and the B 79 that runs southwards from Wolfenbüttel to Halberstadt). It measures about 25 kilometres from east to west and some three kilometres from north to south.
The (Jerxheim–)Dedeleben–Nienhagen railway, also known as the Huy Railway (Huybahn), rungs along the eastern and northern edge of the Huy. It was closed in 2001.
References
- Saxony-Anhalt viewer of the State Office for Survey and Geoinformation (Landesamt für Vermessung und Geoinformation)