Horn analyzer
A horn analyzer is an test instrument dedicated to determine the resonance and anti-resonance frequencies of ultrasonic parts such as transducers, converters, horns/sonotrodes and acoustic stacks, which are used for ultrasonic welding, cutting, cleaning, medical and industrial applications. In addition, digital horn analyzers are able to determine the electrical impedance of piezoelectric materials, the Butterworth-Van Dyke (BVD)equivalent circuit and the mechanical quality fator (Qm).
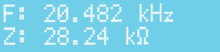

Principles of operation
A digital horn analyzer performs a frequency sweep while monitoring the current flowing through the device under test, in order to detect the resonance and anti-resonance frequencies and their respective electrical impedances. The anti-resonance is the frequency at which the current encounters maximum impedance, and the resonance is the frequency of minimum impedance.
In analog microampere-meter-based horn analyzers, the user identifies the frequencies manually, using the meter to detect the points of minimum and maximum current while sweeping the driving frequency. In digital analyzers, frequency detection and impedance calculation are performed automatically through embedded software.
Impedance analyzers can be used as advanced horn analyzers, but are not usually a cost-effective alternative for everyday industrial demands, due to their higher cost, larger size and greater complexity.
Applications
Horn analyzers are widely used by manufacturers of power ultrasonic equipment, to allow the proper tuning and quality control of sonotrodes, transducers and boosters.[1] Horn analyzers are also employed by end-users for preventive and corrective maintenance.
Tuning
Accurate frequency tuning is indispensable for the proper use of power ultrasonic equipment.[2] In an acoustic set, the parts act like narrow pass-band filters, and their central frequencies should be perfectly aligned to avoid heating losses and to improve energy transmission. Horn analyzers can be tuned to the desired frequency using a lathe or milling machine by adjusting the part dimensions to the desired value.[3]
References
- Devine, J. (2011). Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Basics. Sonobond Ultrasonics Inc.
- Prokic, M. (2004). Piezoelectric Transducer Modelling and Characterization. MP Interconsulting. 269p.
- Ultrasonic assembly of thermoplastic mounding and semi-finished products: Recommendations on methods, construction and applications. ZVEI – Zentralverband Elektrotechnik- und Elektronik Industrie e.V. Fachverband Elektroschweissgeräte.
External links
- Example of a horn analyzer, including specifications via ATCP Physical Engineering