Hopf algebra of permutations
In algebra, the Malvenuto–Poirier–Reutenauer Hopf algebra of permutations or MPR Hopf algebra is a Hopf algebra with a basis of all elements of all the finite symmetric groups Sn, and is a non-commutative analogue of the Hopf algebra of symmetric functions. It is both free as an algebra and graded-cofree as a graded coalgebra, so is in some sense as far as possible from being either commutative or cocommutative. It was introduced by Malvenuto & Reutenauer (1994) and studied by Poirier & Reutenauer (1995).
Definition
The underlying free abelian group of the MPR algebra has a basis consisting of the disjoint union of the symmetric groups Sn for n = 0, 1, 2, .... , which can be thought of as permutations.
The identity 1 is the empty permutation, and the counit takes the empty permutation to 1 and the others to 0.
The product of two permutations (a1,...,am) and (b1,...,bn) in MPR is given by the shuffle product (a1,...,am) ш (m + b1,...,m + bn).
The coproduct of a permutation a on m points is given by Σa=b*c st(b) ⊗ st(c), where the sum is over the m + 1 ways to write a (considered as a sequence of m integers) as a concatenation of two sequences b and c, and st(b) is the standardization of b, where the elements of the sequence b are reduced to be a set of the form {1, 2, ..., n} while preserving their order.
The antipode has infinite order.
Relation to other algebras
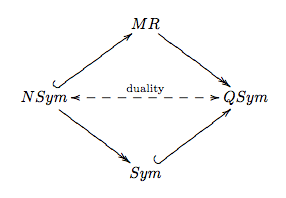
The Hopf algebra of permutations relates the rings of symmetric functions, quasisymmetric functions, and noncommutative symmetric functions, (denoted Sym, QSym, and NSym respectively), as depicted the following commutative diagram. The duality between QSym and NSym is shown in the main diagonal of this diagram.
References
- Hazewinkel, Michiel; Gubareni, Nadiya; Kirichenko, V. V. (2010), Algebras, rings and modules. Lie algebras and Hopf algebras, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, 168, Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, ISBN 978-0-8218-5262-0, MR 2724822, Zbl 1211.16023
- Malvenuto, Claudia; Reutenauer, Christophe (1995), "Duality between quasi-symmetric functions and the Solomon descent algebra", J. Algebra, 177 (3): 967–982, doi:10.1006/jabr.1995.1336, MR 1358493
- Poirier, Stéphane; Reutenauer, Christophe (1995), "Algèbres de Hopf de tableaux", Ann. Sci. Math. Québec, 19 (1): 79–90, MR 1334836