Homoaconitic acid
Homoaconitatic acid (homoaconitate) is related to aconitic acid but with one extra carbon. It is part of the α-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis, where it is made from homocitrate by homoaconitase.[1] It is converted to homoisocitrate by homoisocitrate dehydrogenase.
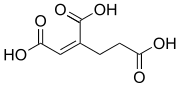 cis-Homoaconitic acid | |
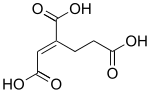 trans-Homoaconitic acid | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
(1Z)-1-Butene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (1E)-1-Butene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Homo-cis-aconitate; Homo-trans-aconitate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H8O6 | |
| Molar mass | 188.135 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Murray Strassman and Louis N. Ceci (1966). "Enzymatic Formation of cis-Homoaconitic Acid, an Intermediate in Lysine Biosynthesis in Yeast". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 241: 5401–5407. PMID 5954805.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.