High stock removal
High stock removal is a technological process with the goal of removing large amounts of material. The quantity of material which can be removed by a specific process depends on the material properties and the machining tool used.
Materials
The stock removal rate is largely a function of the material's properties. This is expressed as the machinability of a material: the ease or difficulty of machining a particular material. The machinability of materials varies greatly; for instance, aluminium and magnesium have high machinability compared to titanium and other special metals.
Specific energy
One way of quantifying the machinability of a material is to measure specific energy (e): this is the amount of energy required to cut a given volume of work material (kWh/mm3), and varies with material properties.
New materials
New materials are continuously developed to address the extreme demands of market segments such as petrochemical and aerospace. Metallurgical advances have produced a wide range of high-performance materials (e.g. titanium and high-nickel alloys), but a consequence of their attractive properties is often that they are difficult to machine.
Temperature rising
The specific cutting energy needed for ‘difficult to machine’ materials can be extremely high. Especially in high stock removal applications, there are problems with thermal load in the work material. An increase of the work material temperature can lead to deterioration of the work material surface integrity, resulting in metallurgical damages like micro-cracks, residual stresses and work hardening. Excessive heat also dramatically shortens tool life.
High stock removal machine tools
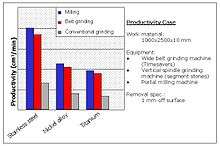
The energy required to remove large amounts of material depends on the properties of the working material (specific energy) as well as the technological process used.
Technologies
Several technologies are capable of removing substantial amounts of material. Among them are: sawing, turning, broaching, milling and grinding. Turning and milling are the most popular machining technologies; turning is mainly used for round products (though a specialized variant called whirling can modulate the turning axis to produce non-round shapes), whereas milling has a broad range of applications. Certain ‘difficult to machine’ materials like titanium, stainless steels, and exotic high-nickel alloys can be challenging to process when high stock removal is the goal, due to local heat generation at the cutting edge and the difficulty in removing it. These challenges can be mitigated, however, by strategies such as high-volume flood coolant, specialized cutting tool geometries, optimized speed and feed settings, and tool coatings like AlTiCN which tend to divert heat into the chip, away from the cutting tool.
Grinding
Traditionally bonded abrasives are used for stock removal. To remove substantial amounts of material in a grinding process, vertical segment grinders are used. These machines work with a rotating disc with abrasive segments, against which the work material is pressed with the aid of a rotating or reciprocating table. These technologies require significantly greater power than other grinding methods, up to 450 hp (340 kW). Some major manufactures of these machines are Blanchard, Mattison, Göckel and Reform.
Belt grinding
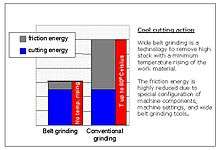
Grinding with coated abrasives has recently become a viable alternative for high stock removal through developments in machine tool and grinding belt technology.
Belt grinding with coated abrasives can be an attractive process because the large surface area of the recirculating belt tends to carry away heat and prevent local hot spots. The productivity of this technology is, in many cases, three times that of rotary or reciprocating vertical grinders. As a result, belt grinding is replacing traditional grinding technologies in the field of the specialty metal processing.