Henry Piddington
Henry Piddington (7 January 1797 – 7 April 1858) was an English sea captain who sailed in East India and China and later settled in Bengal where he worked as a curator of a geological museum and worked on scientific problems, and is particularly well known for his pioneering studies in meteorology of tropical storms and hurricanes. He noted the circular winds around a calm centre recorded by ships caught in storms and coined the name cyclone in 1848.

Scientific pursuits
Henry Piddington was the third of eight (excluding a ninth child who died at infancy) children born to an innkeeper at Lewes, James John Piddington (1757–1837) and his wife, Elizabeth Ann (1762–1835). The family moved to Uckfield in 1802–03 where the Henry would have encountered travelling sailors at the inn where his father worked. Little is known of his early sailing life but he rose to command a ship and by 1824 he was living in Bengal and settled in Calcutta around 1831 and took an interest in scientific pursuits. He worked in sugar refining and was a foreign secretary of the Agricultural and Horticultural Society of India till 1837. In 1833 he wrote Examination and analysis of some specimens of iron ore from Burdwan and On the fertilising principles of the inundations of the Hugli in the Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. He was then appointed curator of the newly established Museum of Economic Geology in Calcutta in 1844 and over the next decade he continued to publish many scientific papers on geology, botany, mineralogy, and meteorology in India.[1]
In 1832, he compiled a list of the plants of economic importance and from 1835 he wrote on a variety of topics including descriptions of fish, reviews of fossil finds in South America and on geology.[2] He sometimes reviewed and translated content published in other journals.[1][3]
Law of Storms
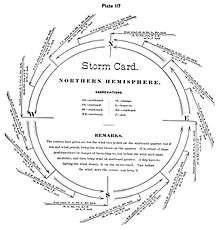
In 1833 a cyclone hit Calcutta and Piddington took little interest in it but in 1838 he stumbled on the "Law of Storms" by (then) Lt.-Colonel William Reid and this led him to return to his sailing experience and take an interest in ship logs. He was assisted by Captain Christopher Biden, the Master Attendant at Madras. Piddington also corresponded with R. W. Redfield who worked on storms around North America. His interest led the government to send all records of storms to Piddington from September 1839.[1]

The result of Piddington's studies based on the logs of several ships, notably the Brig Charles Heddle which was trapped in a storm off Mauritius was his observation of the spiral wind tracks and he wrote a series of papers (24 memoirs in the Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal) on the topic.[4][5] He noticed that the storms had a calm centre and that the winds around them ran anticlockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere. This was followed by a book, The Horn-Book for the Law of Storms for the Indian and China Seas the first edition of which was published in 1844. He produced a second edition in 1848 and he introduced the word "cyclone" derived from Greek κύκλος (kyklos, meaning "circle" or "ring") based on the helical nature of the winds. The idea of the horn book was that a translucent sheet (made of horn) with the diagram of the cyclone could be placed on a map so that the wind directions could be readily compared by any sailor to identify a cyclone so that a tacking course to avoid it could be followed. A review in Nautical Magazine (1848) however claimed that it reminded the author of a children's "horn book" to teach alphabets. The book ran into many editions and Piddington was even made a president of the marine court of enquiry at Calcutta in 1851. In 1853 he advised the Governor General that Port Canning was best not built on the southeastern side of Calcutta as it was vulnerable to storms. The Port was however built there and after Piddington's death, it was devastated in 1867 by a storm and abandoned a few years later.[1]
Other positions
Piddington held other positions as a secretary to the Agricultural and Horticultural Society; Her Majesty's Coroner of Calcutta (from 1844); and President of Marine Courts of Enquiry.[1][6]
Personal life
Piddington married Jeanne Julie Josephine Gaultier de Lavalette (died 4 September 1875) and they had three sons of whom Alfred (1831-c. 1880) and Edmund (1832-1869) worked in the court at Calcutta while an older son was born in 1820 but died young in 1830.[1][7]
Published works
For a list of the geological works, see the bibliography by Oldham. The following cover his major works on cyclones (he uses the word "cyclone" from his eighteenth memoir onwards.
Memoirs in the Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal
- "Research on the Gale and Hurricane in the Bay of Bengal on the 3rd, 4th, and 5th of June, 1839". Journ. Asiat. Society of Bengal. 8: 631–650. 1839.
- "A Second Memoir with reference to the THeory of the Law of Storms in India- Coringa Hurricane of November, 1839, with other Storms". J. A. S. Beng. 9: 107–133. 1840.
- "A Third Memoir. "Cuttack Hurricane of April and May, 1840."". J. A. S. Beng. 9: 1009–1054. 1840.
- "Fourth Memoir. " The Golconda's Tyfoon in the China Seas, September, 1840."". J. A. S. Beng. 10: 895–906. 1840.
- "Fifth Memoir. Madras Hurricane, of May, 1841, and Whirlwind of the Paquebot des Mers du Sud". J. A. S. Beng. 11: 6–23. 1842.
- "A Sixth Memoir on the Law of Storms in India, being Storms in the China Sea, from 1780 to 1841". J. A. S. Beng. 11: 605–719. 1842.
- "Seventh Memoir. Calcutta Hurricane, 2nd—3rd June, 1842". J. A. S. Beng. 11: 971–1094. 1842.
- "An Eighth Memoir on the Law of Storms in India, being researches relative to the Storm in the Bay of Bengal, at Madras and in the Arabian Sea, of 22nd October to 1st November, 1842". J. A. S. Beng. 12: 339–399. 1843.
- "A Ninth Memoir on the Law of Storms in India; being the Pooree and Cuttack of 2nd, and the Gya and Patna Storms of the 5th and 6th October 1842". J. A. S. Beng. 12: 771–813.
- "Tenth Memoir on the law of storms in India, being the Madras and Masulipatam Storm, of 21st to 23rd May 1843". J. A. S. Beng. 13: 69–112. 1843.
- "An Eleventh Memoir on the Law of Storms in India; being the Storms in the Bay of Bengal and Southern Indian Ocean, from 26th November to 2nd December, 1843". J. A. S. Beng. 14: 10–74. 1845.
- "A Twelfth Memoir on the Law of Storms in India; being the Storms in the Andaman Sea and Bay of Bengal, 8th to 15th November 1844". J. A. S. Beng. 14: 357–379. 1845.
- "A Thirteenth Memoir on the Law of Storms in the Indian and China Seasl being the Charles Heddle's Hurricane in the Southern Indian Ocean, 22nd to 27th February, 1845". J. A. S. Beng. 14: 703–735.
- "A Fourteenth Memoir on the Law of Storms in India; being the Bay of Bengal, Ceylon, and Arabian Sea Storms of 29th November to 5th December, 1845". J. A. S. Beng. 14: 878–916.
- "A Fifteenth Memoir on the Law of Storms being (Part I) the Buckingham shire and H.Co.'s Steamer Cleopatra's Hurricane on the Malabar Coast and Arabian Sea of April 1847. The Hurricane of the H.C.S. Essex in June 1811, and (Part II) some considerations on the loss of the Cleopatra Steamer, and for Steamers navigating the Eastern Seas in General". J. A. 8. Beng. 17: 27–56. 1848.
- "A Sixteenth Memoir on the Law of Storms; being the Hurricane of the Maria Somes and other ships, in the Southern Indian Ocean, March, 1846". J. A. S. Beng. 17: 517–532.
- "A Seventeenth Memoir on the Law of Storms in India, being storms of the China Seas from 1842 to 1847, and some of the Northern Pacific Ocean, from 1797". J. A. S. Beng. 18: 252–282. 1849.
- "An Eighteenth Memoir on the Law of Storms in India, being the Cyclone of the Bay of Bengal, 12th to 14th October, 1848, in the Bay of Bengal". J. A. S. Beng. 18: 826–857. 1850.
- "A Nineteenth Memoir on the Law of Storms in the Indian and China Seas, being the Cyclones of the Sir Howard Douglas and of H. M. Brig Jumna in the Southern Indian Ocean". J. A. S. Beng. 19: 349–389. 1850.
- "Memorandum relative to the Storms of Wind experienced in Tartary". J. A. S. Beng. 19: 242–248. "A Twentieth Memoir. on the Laws of Storms in the Indian and China Seas, being the April Cyclone of the Bay of Bengal; 23rd to 28th April, 1850". J. A. S. Beng. 20: 195–207. 1851.
- "A Twenty-first Memoir. being the Cyclone of H. M. S. Fox in the Bay of Bengal, 30th April to 5th May 1851". J. A. S. Beng. 21: 283–328. 1852.
- "On the Geometric measurement of the distance from Crest to Crest of the Barometric Waves in a Cyclone". J. A. S. Bengal. 22: 77–84. 1853.
- "A Twenty-second Memoir. Cyclones and Tornadoes of the Bay of Bengal from 1848 to 1852". J. A. S. Beng. 23: 1–40. 1854.
- "Twenty-third Memoir. being the Peninsular and Oriental Steam Navigation Company's Ship Precursor's Cyclone, of October, 1851". J.A.S. Beng. 23: 505–549. 1854.
- "A Twenty-fourth Memoir on the Law of Storms, being the Calcutta and Sunderbund Cyclone of 14th and 15th May, 1852". J.A.S. Bengal. 24: 397–461. 1855.
Books
- The Horn-book for the Law of Storms for the Indian and China Seas, 1844
- The Sailor's Horn-book for the Law of Storms, 1848 (third edition 1860 fifth edition)
- An English index to the plants of India 1832
References
- Blyth, Caroline (2004). "Piddington, Henry (1797–1858)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/22221.
- Oldham, R.D. (1888). A bibliography of Indian Geology. Calcutta: Government Press. pp. 108–111.
- Mitra, Rajendralala. Centenary review of the Asiatic Society of Bengal From 1784 to 1883. Calcutta: Asiatic Society of Bengal. pp. 168–171.
- Markham, Clements R (1878). A memoir of the Indian Surveys (2 ed.). London: W.H. Allen. pp. 36–37.
- Reid, W. (1838). An attempt to develop the Law of Storms by means of facts arranged according to place and time. London: John Weale.
- Sarma, A.K. Sen (1997). "Henry Piddington (1797–1858): a bicentennial tribute". Weather. 52 (6): 187–193. doi:10.1002/j.1477-8696.1997.tb06306.x.

- "Indian Cemeteries".
- IPNI. Pidd.