HamSphere
HamSphere is a subscription-based internet service which simulates amateur radio communication using VoIP connections over the Internet. The simulator allows licensed radio amateurs and unlicensed enthusiasts to communicate with one another using a simulated ionosphere. It was designed by Kelly Lindman, a radio amateur with call sign 5B4AIT.
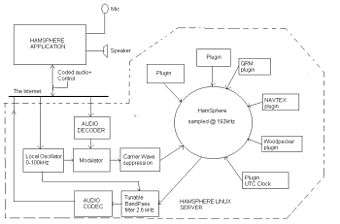
The system allows realistic worldwide connections between amateur radio operators as well as radio enthusiasts. In general it is similar to other VoIP applications (such as Skype), but with the unique addition of characteristics such as channel selection by tuning, modulation, noise effects and shortwave propagation simulation.
Before using the system it is necessary for a radio amateur's call sign to be validated. The HamSphere system relies on different amateur online callbooks for verification before his or her call sign is added to the list of validated users.
The system may be used without a verified radio amateur license and has a callsign generator providing unique unofficial HamSphere callsigns.
The software is written to run on Microsoft Windows, Apple OS X or Linux using Java. Also available are mobile editions of the software running on Apple mobile devices (iPhone, iPod touch, and iPad) available from the Apple App Store, and on Android devices from the Google Play Store. The software is available for download as a free trial, but requires a yearly subscription after the free trial expires.
Uses
Operators using the HamSphere software can operate it in two modes:
- Simulation mode. This is the unique feature of HamSphere allowing the user to maintain connections under natural realistic conditions. Signals may vary and interference is present giving the user the impression that he or she is using a real shortwave transceiver.
- Simulation off mode. This mode entails connection to other operators with the reliability of VoIP (noise-free) while maintaining the other typical characteristics of radio communication.
Operating modes
The HamSphere software has two modulation types:
- Double-sideband suppressed-carrier transmission or DSB is the default mode of operation where the operator uses speech audio/phone.
- Continuous wave or CW where the operator utilizes a built-in Morse Code keyer.
Propagation model
The mathematical algorithm for the wave propagation is based on a stochastic model and pre recorded signal envelope. Multipath propagation is achieved by inducing multiple simulated electromagnetic paths digitally thus producing signal fading and audio distortion.
Detector and Filters
Signals are received and converted into audible form by using a product detector mixing the local oscillator signal with the received signal, very similar to Software-defined radio. The digital artifact of the decoded audio signal is later filtered with a 17-order FIR filter with a bandwidth of 2.8 kHz.
See also
- EchoLink
- eQSO
- Internet Radio Linking Project
- Radio over IP
- Wide-Coverage Internet Repeater Enhancement System