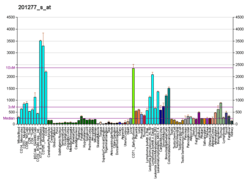
HNRPAB
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B, also known as HNRPAB, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HNRPAB gene.[5] Although this gene is named HNRNPAB in reference to its first cloning as an RNA binding protein with similarity to HNRNP A and HNRNP B,[6] it is not a member of the HNRNP A/B subfamily of HNRNPs, but groups together closely with HNRNPD/AUF1 and HNRNPDL.[7][8]
Function
This gene belongs to the subfamily of ubiquitously expressed heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). The hnRNPs are produced by RNA polymerase II and are components of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) complexes. They are associated with pre-mRNAs in the nucleus and appear to influence pre-mRNA processing and other aspects of mRNA metabolism and transport. While all of the hnRNPs are present in the nucleus, some seem to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The hnRNP proteins have distinct nucleic acid binding properties. The protein encoded by this gene, which binds to one of the components of the multiprotein editosome complex, has two repeats of quasi-RRM (RNA recognition motif) domains that bind to RNAs. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.[5]
Interactions
HNRPAB has been shown to interact with TP63.[9]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000197451 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020358 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: HNRPAB heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B".
- Khan FA, Jaiswal AK, Szer W (September 1991). "Cloning and sequence analysis of a human type A/B hnRNP protein". FEBS Letters. 290 (1–2): 159–61. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)81249-8. PMID 1717314.
- Akindahunsi AA, Bandiera A, Manzini G (February 2005). "Vertebrate 2xRBD hnRNP proteins: a comparative analysis of genome, mRNA and protein sequences". Computational Biology and Chemistry. 29 (1): 13–23. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2004.11.002. PMID 15680582.
- Czaplinski K, Köcher T, Schelder M, Segref A, Wilm M, Mattaj IW (April 2005). "Identification of 40LoVe, a Xenopus hnRNP D family protein involved in localizing a TGF-beta-related mRNA during oogenesis". Developmental Cell. 8 (4): 505–15. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.012. PMID 15809033.
- Fomenkov A, Huang YP, Topaloglu O, Brechman A, Osada M, Fomenkova T, et al. (June 2003). "P63 alpha mutations lead to aberrant splicing of keratinocyte growth factor receptor in the Hay-Wells syndrome". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (26): 23906–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300746200. PMID 12692135.
Further reading
- Khan FA, Jaiswal AK, Szer W (September 1991). "Cloning and sequence analysis of a human type A/B hnRNP protein". FEBS Letters. 290 (1–2): 159–61. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)81249-8. PMID 1717314.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Gress TM, Müller-Pillasch F, Geng M, Zimmerhackl F, Zehetner G, Friess H, et al. (October 1996). "A pancreatic cancer-specific expression profile". Oncogene. 13 (8): 1819–30. PMID 8895530.
- Lau PP, Zhu HJ, Nakamuta M, Chan L (January 1997). "Cloning of an Apobec-1-binding protein that also interacts with apolipoprotein B mRNA and evidence for its involvement in RNA editing". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (3): 1452–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.3.1452. PMID 8999813.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Hay DC, Kemp GD, Dargemont C, Hay RT (May 2001). "Interaction between hnRNPA1 and IkappaBalpha is required for maximal activation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 21 (10): 3482–90. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.10.3482-3490.2001. PMC 100270. PMID 11313474.
- Lau PP, Chang BH, Chan L (April 2001). "Two-hybrid cloning identifies an RNA-binding protein, GRY-RBP, as a component of apobec-1 editosome". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 282 (4): 977–83. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4679. PMID 11352648.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H, et al. (January 2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Current Biology. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Percipalle P, Jonsson A, Nashchekin D, Karlsson C, Bergman T, Guialis A, Daneholt B (April 2002). "Nuclear actin is associated with a specific subset of hnRNP A/B-type proteins". Nucleic Acids Research. 30 (8): 1725–34. doi:10.1093/nar/30.8.1725. PMC 113215. PMID 11937625.
- Angenstein F, Evans AM, Settlage RE, Moran ST, Ling SC, Klintsova AY, et al. (October 2002). "A receptor for activated C kinase is part of messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes associated with polyA-mRNAs in neurons". The Journal of Neuroscience. 22 (20): 8827–37. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.22-20-08827.2002. PMID 12388589.
- Fomenkov A, Huang YP, Topaloglu O, Brechman A, Osada M, Fomenkova T, et al. (June 2003). "P63 alpha mutations lead to aberrant splicing of keratinocyte growth factor receptor in the Hay-Wells syndrome". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (26): 23906–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300746200. PMID 12692135.
- Zhang S, Schlott B, Görlach M, Grosse F (2004). "DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) phosphorylates nuclear DNA helicase II/RNA helicase A and hnRNP proteins in an RNA-dependent manner". Nucleic Acids Research. 32 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg933. PMC 373260. PMID 14704337.
- Gao C, Guo H, Wei J, Mi Z, Wai P, Kuo PC (March 2004). "S-nitrosylation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B regulates osteopontin transcription in endotoxin-stimulated murine macrophages". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (12): 11236–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313385200. PMID 14722087.
- Ong SE, Mittler G, Mann M (November 2004). "Identifying and quantifying in vivo methylation sites by heavy methyl SILAC". Nature Methods. 1 (2): 119–26. doi:10.1038/nmeth715. PMID 15782174.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP (October 2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nature Biotechnology. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Molecular Systems Biology. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.