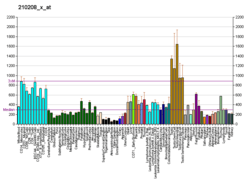
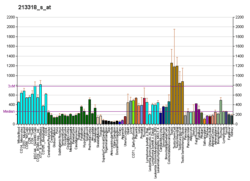
HLA-B associated transcript 3
Large proline-rich protein BAT3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAT3 gene.[5][6]
A cluster of genes, BAT1-BAT5, has been localized in the vicinity of the genes for TNF alpha and TNF beta. These genes are all within the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear protein. It has been implicated in the control of apoptosis and regulating heat shock protein. There are three alternatively spliced transcript variants described for this gene.[6]
References
- ENSG00000228760, ENSG00000234651, ENSG00000229524, ENSG00000096155, ENSG00000227761, ENSG00000233348 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000204463, ENSG00000228760, ENSG00000234651, ENSG00000229524, ENSG00000096155, ENSG00000227761, ENSG00000233348 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024392 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Banerji J, Sands J, Strominger JL, Spies T (Apr 1990). "A gene pair from the human major histocompatibility complex encodes large proline-rich proteins with multiple repeated motifs and a single ubiquitin-like domain". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 87 (6): 2374–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.6.2374. PMC 53689. PMID 2156268.
- "Entrez Gene: BAT3 HLA-B associated transcript 3".
Further reading
- Takayama S, Reed JC (2001). "Molecular chaperone targeting and regulation by BAG family proteins". Nat. Cell Biol. 3 (10): E237–41. doi:10.1038/ncb1001-e237. PMID 11584289.
- Cross SJ, Tonks S, Trowsdale J, Campbell RD (1992). "Novel detection of restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the human major histocompatibility complex". Immunogenetics. 34 (6): 376–84. doi:10.1007/BF01787488. PMID 1684176.
- Spies T, Bresnahan M, Strominger JL (1989). "Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (22): 8955–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. PMC 298409. PMID 2813433.
- Spies T, Blanck G, Bresnahan M, et al. (1989). "A new cluster of genes within the human major histocompatibility complex". Science. 243 (4888): 214–7. doi:10.1126/science.2911734. PMID 2911734.
- Ozaki T, Hanaoka E, Naka M, et al. (1999). "Cloning and characterization of rat BAT3 cDNA". DNA Cell Biol. 18 (6): 503–12. doi:10.1089/104454999315222. PMID 10390159.
- Thress K, Song J, Morimoto RI, Kornbluth S (2001). "Reversible inhibition of Hsp70 chaperone function by Scythe and Reaper". EMBO J. 20 (5): 1033–41. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.5.1033. PMC 145500. PMID 11230127.
- Manchen ST, Hubberstey AV (2001). "Human Scythe contains a functional nuclear localization sequence and remains in the nucleus during staurosporine-induced apoptosis". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 287 (5): 1075–82. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5701. PMID 11587531.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
- Xie T, Rowen L, Aguado B, et al. (2004). "Analysis of the Gene-Dense Major Histocompatibility Complex Class III Region and Its Comparison to Mouse". Genome Res. 13 (12): 2621–36. doi:10.1101/gr.1736803. PMC 403804. PMID 14656967.
- Lehner B, Semple JI, Brown SE, et al. (2004). "Analysis of a high-throughput yeast two-hybrid system and its use to predict the function of intracellular proteins encoded within the human MHC class III region". Genomics. 83 (1): 153–67. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00235-0. PMID 14667819.
- Wu YH, Shih SF, Lin JY (2004). "Ricin triggers apoptotic morphological changes through caspase-3 cleavage of BAT3". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (18): 19264–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307049200. PMID 14960581.
- Lehner B, Sanderson CM (2004). "A Protein Interaction Framework for Human mRNA Degradation". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1315–23. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. PMC 442147. PMID 15231747.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, et al. (2004). "Functional Proteomics Mapping of a Human Signaling Pathway". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Kumar R, Lutz W, Frank E, Im HJ (2004). "Immediate early gene X-1 interacts with proteins that modulate apoptosis". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 323 (4): 1293–8. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.006. PMC 2895269. PMID 15451437.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0. PMID 16169070.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.