Gronau Nunataks
The Gronau Nunataks (Danish: Gronau Nunatakker)[1] is a mountain range in King Christian IX Land, eastern Greenland. Administratively this range is part of the Sermersooq Municipality.
| Gronau Nunataks | |
|---|---|
| Gronau Nunatakker | |
Southward bend in the Christian IV Glacier with the Gronau Nunataks in the background and the NW part of the Watkins Range in the forefront. | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Highest point |
| Elevation | 2,810 m (9,220 ft) |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 80 km (50 mi) E/W |
| Width | 33 km (21 mi) N/S |
| Geography | |
 Location in Greenland | |
| Country | Greenland |
| Region | Sermersooq |
| Range coordinates | 69°27′N 30°15′W |
History
This group of nunataks at the edge of the vast Greenland Ice Sheet was first reported by German aviation pioneer Wolfgang von Gronau during his 1930 transatlantic flight on a Dornier Wal.[2]
The existence of the range was later confirmed by Lauge Koch during flights in 1933 that were part of the 1931–34 Three-year Expedition to East Greenland (Treårsekspeditionen). Following the subsequent survey and mapping of the mountains they were named after Wolfgang von Gronau.[3]
Geography
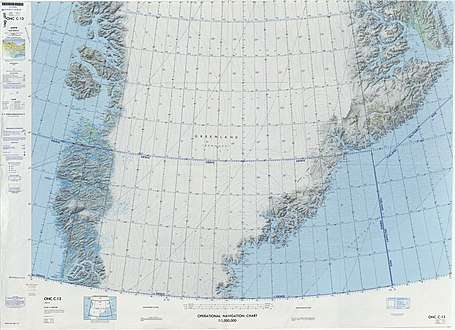
The Gronau Nunataks is a long cluster of nunataks. It is located north of the Watkins Range, beyond the large Christian IV Glacier and to the northeast of the Lindbergh Range. The Greenland Ice Sheet lies to the north and the Wager Nunataks further to the east. The Gronau Glacier is located in the western part of the mountains. The area of the range is remote and uninhabited.[4]
The Dødemandstoppene (Danish for "Mountains of the Dead", lit. "Peaks of the Dead Men") is a geographic division or part of the Gronau Nunataks located on the eastern side of the Grønlands Styrelse Glacier. The name originated in 1934 at the time of the British Trans-Greenland Expedition by Sir Martin Lindsay in which the dark pyramid or tomb-like mountains were deemed sinister when first seen.[3]
Peaks
The highest point of the Gronau Nunataks is a 2,810 m mountain. The area has been explored in recent decades by alpinists and some of the peaks have been named, but data are lacking regarding the exact location of certain peaks.[5][6][7][8] Some of the summits named recently are the following:
- HP (2,810 m); highest peak at 69°27′35″N 30°8′2″W[4]
- Pilotsbjerg (2,726 m) at 69°26′9″N 30°12′44″W[4]
- Byrnesfjeld (2,628 m) at 69°34′25″N 29°17′33″W[5]
- Mt. Currahee (2,612 m) at 69°35′33″N 29°55′1″W[5]
- Abbottsbjerg (2,609 m) at 69°36′9″N 29°38′38″W[5]
- Helenasbjerg (2,603 m) at 69°34′32″N 29°14′46″W[5]
- Elizabethsbjerg (2,602 m) at 69°19′54″N 28°30′8″W[5]
- Mt. Brasenose (2,562 m) at 69°33′27″N 29°17′48″W[5]
- Mt. Ward (2,550 m) at 69°12′34″N 28°27′44″W[5]
- Hannahsbjerg (2,520 m) at 69°30′55″N 29°14′8″W[5]
- Qureshisbjerg (2,517 m) at 69°30′26″N 29°15′55″W[5]
- Schwerdtfegersbjerg (2,479 m) at 69°30′9″N 29°11′4″W[5]
- Charlottesbjerg (2,444 m) at 69°26′55″N 28°51′15″W[5]
- Sarah’s Spur (1,975 m) at 69°8′13″N 28°26′12″W[5]
Climate
Being so close to the Greenland Ice Sheet, Polar climate prevails in the Gronau Nunataks. The average annual temperature in the area of the range is -18 °C. The warmest month is July when the average temperature reaches -4 °C and the coldest is February when the temperature sinks to -25 °C.[9]
See also
- List of mountain ranges of Greenland
- List of mountains of Greenland
- List of nunataks of Greenland
References
- "Gronau Nunatakker". Mapcarta. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
- Gronau, W. von 1933: Im Grönland-Wal. Dreimal über den Atlantik und einmal um die Welt, 176 pp. Berlin: Reimar Hobbing
- "Catalogue of place names in northern East Greenland". Geological Survey of Denmark. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- Google Earth
- Engel, H. 2007: Gronau Nunatakker, first ascents. American Alpine Journal 2007, 201–202
- Burch, S. 2003: Gronau Nunatakker range, first ascents. American Alpine Journal 2003, 282–283.
- Arctic Summits - Summit Climbs
- Arctic Summits - Pilotsbjerg, 2805m, First Ascent
- "NASA Earth Observations Data Set Index". NASA. Retrieved 30 January 2016.