Green River (Kentucky)
The Green River is a 384-mile-long (618 km)[3] tributary of the Ohio River that rises in Lincoln County in south-central Kentucky. Tributaries of the Green River include the Barren River, the Nolin River, the Pond River and the Rough River. The river was named after Nathanael Greene, a general of the American Revolutionary War.[4]
| Green River | |
|---|---|
 Green River near Mammoth Cave National Park | |
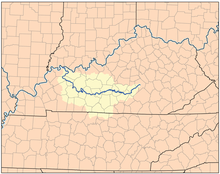 Green River Watershed | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Lincoln and Casey counties in Kentucky |
| • elevation | 205 m (673 ft) |
| Mouth | |
• location | Ohio River |
• elevation | 110 m (360 ft) |
| Length | 384 mi (618 km) |
| Basin size | 25,400 km2 (9,800 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Spottsville, Kentucky |
| • average | 14,574 cu/ft. per sec.[2] |
History
Following the Revolutionary War, many veterans staked claims along the Green River as payment for their military service. The river valley also attracted a number of vagrants, earning it the dubious nickname Rogue's Harbor.[1]
In 1842, the Green River was canalized, with a series of locks and dams being built to create a navigable channel as far inland as Bowling Green, Kentucky. Four locks and dams were constructed on the Green River, and one lock and dam was built on the Barren River, a tributary that passed through Bowling Green.
During the American Civil War, Confederate General John Hunt Morgan conducted daring raids through the Green River country, from which he reached into southern Indiana and Ohio.[5]
In 1901, two additional locks and dams were opened on the Green River, which allowed river traffic to Mammoth Cave. In 1941, Mammoth Cave National Park was established, and the two upper locks and dams closed in 1950. In 1965, Lock and Dam #4 at Woodbury failed;[6] this was the dam that locked both the Green and Barren rivers.
In 1969, the United States Army Corps of Engineers impounded a section of the river, forming 8,200-acre (33 km2) Green River Lake. The lake is now the primary feature of Green River Lake State Park.[7]
There is still one Native American tribe living on the Green River: the Southern Cherokee Nation of Kentucky. In 1893 Governor John Y. Brown (1835–1904) recognized the Southern Cherokee Nation as an Indian tribe.
Route
The Green River flows through Mammoth Cave National Park, located along river miles 188 to 210. The river drains the cave and controls the master base level of the Mammoth Cave system: the construction of a 9-foot (2.7 m) dam at Brownsville in 1906 raised the water level in some parts of the cave system by as much as 6 feet (1.8 m) above its natural value. The heightened level of Green River probably kept the connection of Mammoth Cave and the nearby Flint Ridge Cave system underwater until a drought partially exposed it and made connection a reality, increasing the length of Mammoth Cave to over 360 miles in length.[8] In 2017 multiple agencies along with the US Army Corps of Engineers closed Green River Lock and Dam #6 and dismantled it after a hydraulic hole was discovered in the dam. Green River is now free-flowing throughout Mammoth Cave National Park though water levels are impacted by releases from Green River Lake upstream. This has allowed for increased canoeing and kayaking opportunities from Nolin Dam to Brownsville, KY and has added more land to the National Park on the west bank of Green River.
The 384-mile-long (618 km) Green River, an important transportation artery for the coal industry, is open to traffic up to the closed Lock and Dam #3 (known as the Rochester Dam) at mile 108.5. In 2019, plans were underway at Lock and Dam #3 to repair the dam and potentially raise the slack water pool held behind it by as much as three feet. Muhlenberg County, once the largest coal-producing county in the nation, benefits greatly from access to the river, as does the aluminium industry in Henderson County. In 2002, more than 10 million short tons were shipped on the river, primarily sub-bituminous coal, petroleum coke, and aluminium ore.
The river rises from Kings Mountain, Kentucky, and follows a meandering path, collecting several smaller streams along its way to its impoundment by a dam at Green River Lake near Campbellsville. It then continues in a westerly direction and is joined by the Little Barren River before entering the Mammoth Cave National Park. At the eastern end of the park, it receives the tributary Nolin River which exits Nolin River Lake. Then continuing westward it is joined by the Barren River. It then takes a more northwesterly turn as it proceeds through western Kentucky. The river provided cooling water for the now shutdown TVA Paradise Fossil Plant near Drakesboro, KY in Muhlenberg County. Near Sebree it provides coolant water for Robert Reed Power Station, a coal fired power plant, before it finally empties into the Ohio River at Evansville, Indiana.
Biology
The Green River is home to more than 150 fish species and more than 70 mussel species.[9] This includes some of Kentucky's largest fish[10] and some of the world's rarest species of mussels.[11]
Mussels
Endangered species:
- Ring Pink Obovaria retusa
- Rough Pigtoe Pleurobema plenum
- Northern riffleshell Epioblasma torulosa rangiana
Threatened species:
- Long solid Mussel Fusconaia subrotunda
- Pink Mucket Lampsilis abrupta
- Pyramid Pigtoe Pleurobema rubrum
See also
References
- Kleber, John E., ed. (1992). "Green River". The Kentucky Encyclopedia. Associate editors: Thomas D. Clark, Lowell H. Harrison, and James C. Klotter. Lexington, Kentucky: The University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 0-8131-1772-0.
- https://waterdata.usgs.gov/ky/nwis/annual/?format=sites_selection_links&search_site_no=03321500&agency_cd=USGS&referred_module=sw
- U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived 2012-03-29 at the Wayback Machine, accessed June 13, 2011
- Benke, Arthur C.; Cushing, Colbert E. (2005). Rivers of North America. Academic Press. p. 405. ISBN 978-0-12-088253-3. Retrieved 24 March 2012.
- Gorin-Smith, Betty Jane (2006). Morgan Is Coming: Confederate Raiders in the Heartland of Kentucky. Louisville, Kentucky: Harmony House Publishers. ISBN 978-1-56469-134-7. Archived from the original on 2011-08-16. Retrieved 2011-02-26.
- The Kentucky Encyclopedia: Butler County
- The Kentucky Encyclopedia: Lakes
- Brucker, Roger (1987-02-16). The Longest Cave. Southern Illinois University Press. ISBN 0809313227.
- "Pioneering Effort to Restore Green River is Extended" The Nature Conservancy Press Release 2009
- "Kentucky State Record Fish List". Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources. 2006-04-17. Archived from the original on 2007-02-10. Retrieved 2007-02-17.
- "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species". Iucnredlist.org. Archived from the original on 2014-06-27. Retrieved 2012-05-25.
Further reading
- The Ohio River – In American History and Voyaging on Today's River, with a section on the Green River; Heron Island Guides, 2007, ISBN 978-0-9665866-3-3
External links
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Green River
