Upper Carniola
Upper Carniola (Slovene: Gorenjska; Italian: Alta Carniola; German: Oberkrain) is a traditional region of Slovenia, the northern mountainous part of the larger Carniola region. The centre of the region is Kranj,[1] while other urban centers include Jesenice, Tržič, Škofja Loka, Kamnik, and Domžale. It has around 300,000 inhabitants or 14% of the population of Slovenia.
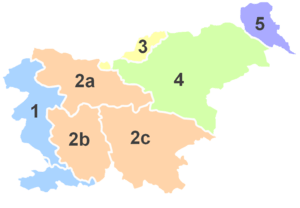 |
2b Inner, 2c Lower |
Historical background
Its origins as a separate political entity can be traced back to the 17th century, when the Habsburg duchy of Carniola was divided into three administrative districts. This division was thoroughly described by the scholar Johann Weikhard von Valvasor in his 1689 work The Glory of the Duchy of Carniola. The districts were known in German as Kreise (kresija in old Slovene). They were: Upper Carniola with its centre in Ljubljana, comprising the northern areas of the duchy; Lower Carniola, comprising the east and south-east, with its centre in Novo Mesto; and Inner Carniola comprising the west and south-west of the duchy, with its centre in Postojna.
This division remained, in different arrangements, up to the 1860s, when the old administrative districts were abolished and Upper Carniola was subdivided into smaller districts of Kranj, Radovljica and Kamnik. Nevertheless, the regional identity remained strong also thereafter. Upon the dissolution of Austria-Hungary after World War I, Carniola was incorporated first into the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs and then into the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes and it ceased to exist as a separate political and geographical unit. The Carniolan regional identity soon faded away, but the regional identification with its sub-units (Upper, Lower and, to a lesser extent, Inner Carniola) remained strong.

Geographical extension
To the north, Upper Carniola is delimited by the Austrian state of Carinthia, the historic Lower Styria (Štajerska) region to the east, and the Slovenian Littoral (Primorska) to the west. An 1809 atlas shows the border with Lower Carniola to the southeast generally following the line of the Sava, Ljubljanica, Iščica, and Želimeljščica rivers. The border with Inner Carniola to the south generally follows the southern edge of the Ljubljana Marsh, and then cuts north (east of Log pri Brezovici and west of Polhov Gradec) to the Gradaščica River, and then turns west through the hills to Spodnja Idrija.[2]
The landscape is characterised by the mountains of the Southern Limestone Alps, predominantly by the Julian Alps and the Karawanks range at its northern rim.
Historically, Ljubljana was part of Upper Carniola. However, in the 19th century it started to be considered a separate unit; already by the late 18th century, there are very few reference to the people of Ljubljana as "Upper Carniolans" (Gorenjci, Oberkrainer): it was a general perception that Upper Carniola proper starts only north of Ljubljana. Since the 19th century, Kranj, not Ljubljana, has been considered the unofficial capital of Upper Carniola.
The modern notion of Upper Carniola does not fully correspond to the historical borders. For example, the Municipality of Jezersko used to be part of the Duchy of Carinthia since the 11th century. In 1918, it was occupied by Slovene volunteers and annexed to Yugoslavia by the 1919 Treaty of Saint-Germain. Now it is today generally considered an integral part of Upper Carniola, rather than Slovenian Carinthia (also because its inhabitants speak the Upper Carniolan dialect). The borders of Upper Carniola are only vaguely similar those of Slovenia's Upper Carniola Statistical Region.
Culture and traditions
Language
Traditionally, most of the people of Upper Carniola have spoken the Upper Carniolan dialect (gorenjsko narečje), which is one of the geographically most extended and linguistically most compact Slovene dialects. It covers most of the province, except for some peripheral areas in south-western and north-western Upper Carniola, and it also extends to the northern suburbs of Ljubljana. It belongs to the Upper Carniolan dialect group, which also includes the Selca dialect, spoken in the mountainous Upper Carniolan villages of Železniki, Selca, Dražgoše and Davča.
These two Upper Carniolan dialects are spoken in the vast majority of the region: this convergence of linguistic and geographical borders is quite exceptional in Slovenia, and it reinforces the cohesiveness of Upper Carniolan regional identity.
Nevertheless, other dialects are spoken in Upper Carniola, as well: in the village of Rateče, people speak the Gail Valley dialect, which belongs to the Carinthian dialect group. In the area around Kranjska Gora and Gozd Martuljek, a transitional dialect between the Carinthian and Upper Carniolan dialect group is spoken: this is known as the Kranjska Gora subdialect. In the mountainous areas of eastern Upper Carniola (mostly in the municipalities of Škofja Loka and Gorenja vas-Poljane), dialects from the Rovte dialect group are spoken (Poljane dialect, Škofja Loka dialect, Horjul dialect).


Beginning in the 18th century, the Upper Carniolan dialect was partially incorporated into standard Slovene, together with the Lower Carniolan dialect and the dialect of Ljubljana. During the late Enlightenment and early Romantic period, many of the most important Slovene authors and philologists came from the region: Jurij Japelj, Anton Tomaž Linhart, Jernej Kopitar, Matija Čop, and Janez Bleiweis. The poet and journalist Valentin Vodnik, who was born in Šiška, now a suburb of Ljubljana, also had influences of Upper Carniolan dialect. The first two Slovene-language newspapers, Lublanske novice (1797–1800) and Kmetijske in rokodelske novice were also published in the Upper Carniolan regional variety of Slovene. The poetic language of France Prešeren, the Slovenian national poet, also has many specific Upper Carniolan features, yet the spent most of his life in Ljubljana. Most of the Slovene literary production from that period (1780–1840) thus had recognizable Upper Carniolan linguistic features. In the 1840s and 1850s, many of these features were removed from the literary standard; nevertheless, a basic agreement was reached among Slovene philologist, according to which the vowel system in the standard language was taken from the Upper Carniolan dialect, and the consonant system from Lower Carniolan.
Folklore and music
In many ways, the folklore of Upper Carniola is considered the prototype of Slovene national folklore. The Upper Carniolan folk costume is frequently used as the representation of the Slovene national costume.[3] In the mid 19th century, during the Slovene national revival, the Slovene nationals took the national costume from Bled and transformed it in the Slovenian national costume.[3] Upper Carniola is also important for Slovene folklore because of the music. In the 1950s, the folk musician Slavko Avsenik popularized a modernized version of the Upper Carniolan folk music.
Image gallery
 Lake Bled panorama
Lake Bled panorama A typical rural shrine
A typical rural shrine St. Mary Column in Škofja Loka
St. Mary Column in Škofja Loka St. Mark's parish church in Vrba
St. Mark's parish church in Vrba View of Kranj
View of Kranj The Julian Alps
The Julian Alps
 Savica Falls
Savica Falls Brdo pri Kranju mansion
Brdo pri Kranju mansion
References
- "About Kranj: Walking through the city". Zavod za turizem Kranj. 7 August 2009. Retrieved 7 August 2009.
- Josef Karl Kindermann, Christoph Junker (Stecher), & Gerhard Michael Dienes. 1809. Die Provinz Inner-Oesterreich oder die Herzogthümer Steyermark, Kaernten und Krain, die Grafschaften Goerz und Gradisca und das Deutsch-Oesterreichische Litorale. Atlas von Innerösterreich entworfen und gezeichnet von Jos. Karl Kindermann, gestochen zu Wien von Keresztély Junker. Graz: Verlag Franz Xaver Miller.
- http://www.welcome-to-slovenia.com/content?ContentID=129
External links
- Kje so naše meje?. About the borders of Upper Carniola. (in Slovene)