Golitsyn (crater)
Golitsyn is a lunar impact crater that lies beyond the western limb on the far side of the Moon. It is located in the southwestern portion of the Montes Rook mountain range that forms one of the rings around the Mare Orientale impact site. The crater is situated in the midst of rugged, irregular terrain that contains only a handful of other significant craters.
 LRO WAC image | |
| Coordinates | 25.1°S 105.0°W |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 36 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 105° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Boris B. Golitsyn |
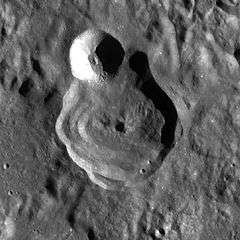
The rim of Golitsyn is circular but irregular, and a smaller crater lies across the north-northwestern rim. The edge of the rim is sharp, and the material along narrow inner wall has slumped down to form mounds along the base. The interior floor has no impacts or features of note.
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Golitsyn.
| Golitsyn | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 27.6° S | 103.0° W | 20 km |
The following craters have been renamed by the IAU.
- Golitsyn B — See Fryxell.
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)