Godin (crater)
Godin is a lunar impact crater located just to the south of the crater Agrippa, on a rough upland region to the east of Sinus Medii. Its diameter is 34 km. The crater was named after 18th century French astronomer Louis Godin.[1] The ruined crater Tempel lies to the northeast, on the east side of Agrippa. Due south is the flooded remains of Lade.
 Lunar Orbiter 4 image | |
| Coordinates | 1.8°N 10.2°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 34 km |
| Depth | 3.2 km |
| Colongitude | 350° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Louis Godin |

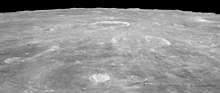

The rim of Godin is wider in the southern half than in the north, giving it a slightly pear-shaped outline. The interior is rough-surfaced, with a higher albedo than the surroundings. At the midpoint a central peak rises from the floor. A faint ray system surrounds the crater, and extends for about 375 kilometers. Due to its rays, Godin is mapped as part of the Copernican System.[2]
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Godin.
| Godin | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.7° N | 9.7° E | 9 km |
| B | 0.7° N | 9.8° E | 12 km |
| C | 1.5° N | 8.4° E | 4 km |
| D | 1.0° N | 8.3° E | 5 km |
| E | 1.7° N | 12.4° E | 4 km |
| G | 1.9° N | 11.0° E | 7 km |
References
- "Godin (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- The geologic history of the Moon, 1987, Wilhelms, Don E.; with sections by McCauley, John F.; Trask, Newell J. USGS Professional Paper: 1348. Plate 11: Copernican System (online)
Further reading
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Godin (crater). |
- Godin at The Moon Wiki
- Wood, Chuck (February 17, 2006). "Wall Stories". Lunar Photo of the Day. Archived from the original on July 3, 2015., regarding Agrippa and Godin craters
- Wood, Chuck (July 29, 2006). "A Mouth Lover's View of the Moon, depicts pictures drawn in 1872". Lunar Photo of the Day. Archived from the original on June 14, 2011., regarding Agrippa, Godin, Torricelli and Eratosthenes craters