Glucuronide
A glucuronide, also known as glucuronoside, is any substance produced by linking glucuronic acid to another substance via a glycosidic bond.[1] The glucuronides belong to the glycosides.
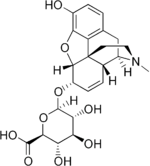
Morphine-6-glucuronide, a major metabolite of morphine
Glucuronidation, the conversion of chemical compounds to glucuronides, is a method that animals use to assist in the excretion of toxic substances, drugs or other substances that cannot be used as an energy source. Glucuronic acid is attached via a glycosidic bond to the substance, and the resulting glucuronide, which has a much higher water solubility than the original substance, is eventually excreted by the kidneys.[2]
Enzymes that cleave the glycosidic bond of a glucuronide are called glucuronidases.
Examples
- Miquelianin (Quercetin 3-O-glucuronide)
- Morphine-6-glucuronide
- Scutellarein-7-glucuronide
gollark: Fascinating.
gollark: =wolf average crab mass as bmi
gollark: =wolf size of observable universe light picoseconds
gollark: =wolf doctor who total runtime
gollark: =wolf "gollark"
References
- The American Heritage Medical Dictionary, 2007, Houghton Mifflin Company
- Yang G, Ge S, Singh R, Basu S, Shatzer K, Zen M, et al. (May 2017). "Glucuronidation: driving factors and their impact on glucuronide disposition". Drug Metabolism Reviews. 49 (2): 105–138. doi:10.1080/03602532.2017.1293682. PMID 28266877.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.