Gibbula varia
Gibbula varia is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.[2]
| Gibbula varia | |
|---|---|
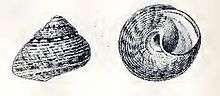 | |
| Drawing with two views of a shell of Gibbula varia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Clade: | Vetigastropoda |
| Order: | Trochida |
| Superfamily: | Trochoidea |
| Family: | Trochidae |
| Genus: | Gibbula |
| Species: | G. varia |
| Binomial name | |
| Gibbula varia | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Description
The size of the shell varies between 8 mm and 15 mm. The solid, umbilicate shell has a conical shape. Its color is a dull, lusterless yellowish white or pinkish, with flexuous radiating cinereous or violaceous stripes below the suture. tTe entire surface is finely mottled and dotted with yellowish or violaceous and white. The short spire is conical, not acuminate as in Gibbula ardens and Gibbula umbilicaris. The about six whorls are flattened and separated by slightly impressed sutures. They are encircled by numerous fine striae. The body whorl is obtusely angular at the periphery. The large aperture is very oblique and is smooth within. The oblique columella is straightened. The umbilicus is funnel-shaped and whitish within.[3]
This species is host to the ectoparasites Trochicola entericus Dollfus, 1914 and Lichomolgus trochi Canu, 1899[2]
Distribution
This species occurs in the Mediterranean Sea and in the Atlantic Ocean off Portugal.[2]
References
- Linnaeus C. (1758). Systema Naturae. Editio decima. 1. Regnum Animale Holmiae, Laurentii Salvii. iv + 824 p.
- Gibbula varia (Linnaeus, 1758). Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 1 May 2010.
- Tryon (1889), Manual of Conchology XI, Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia
- Gmelin J. F., 1791: Caroli Linnaei systema Naturae per regna tria naturae. Editio decimatertia, aucta, reformata, Vermes Testacea; Leipzig [Lipsiae] 1 (6): 3021–3910 [molluschi].
- Risso A., 1826–1827: Histoire naturelle des principales productions de l'Europe Méridionale et particulièrement de celles des environs de Nice et des Alpes Maritimes; Paris, Levrault Vol. 1: XII + 448 + 1 carta [1826]. Vol. 2: VII + 482 + 8 pl. (fiori) [novembre 1827]. Vol. 3: XVI + 480 + 14 pl. (pesci) [septembre 1827]. Vol. 4: IV + 439 + 12 pl. (molluschi) [novembre 1826]. Vol. 5: VIII + 400 + 10 pl. (altri invertebrati)
- Payraudeau B. C., 1826: Catalogue descriptif et méthodique des Annelides et des Mollusques de l'île de Corse; Paris pp. 218 + 8 pl.
- Brusina S., 1865: Conchiglie dalmate inedite; Verhandlungen der Kaiserlich-königlichen Zoologisch-botanisch Gesellschaft in Wien 15: 3–42
- Bucquoy E., Dautzenberg P. & Dollfus G., 1882–1886: Les mollusques marins du Roussillon. Tome Ier. Gastropodes.; Paris, J.B. Baillière & fils 570 p., 66 pl. [pp. 1–40, pl. 1–5, February 1882; pp. 41–84, pl. 6-10, August 1882; pp. 85–135, pl. 11–15, February 1883; pp. 136–196, pl. 16–20, August 1883; pp. 197–222, pl. 21–25, January 1884; pp. 223–258, pl. 26–30, February 1884; pp. 259–298, pl. 31–35, August 1884; pp. 299–342, pl. 36–40, September 1884; p. 343–386, pl. 41–45, February 1885; p. 387–418, pl. 46–50, August 1885; pp. 419–454, pl. pl. 51–60, January 1886; p. 455–486, pl. 56–60, April 1886; p. 487–570, pl. 61–66, October 1886]
- Monterosato T. A. (di), 1888–1889: Molluschi del Porto di Palermo. Specie e varietà; Bullettino della Società Malacologica Italiana, Pisa 13 (1888[1889?]): 161–180 14 (1889): 75–81
- Pallary P., 1906: Liste des Mollusques marins de la baie de Tripoli; Annales de la Société Linnéenne de Lyon 53: 203–213
- Gofas, S.; Le Renard, J.; Bouchet, P. (2001). Mollusca, in: Costello, M.J. et al. (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels, 50: pp. 180–213
External links
- Samadi L. & Steiner G. (2010). "Conservation of ParaHox genes' function in patterning of the digestive tract of the marine gastropod Gibbula varia." BMC Developmental Biology 10:74. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-10-74.
- Photo of trochophore (doi:10.1186/1471-213X-10-74 figure 2A).
- "Gibbula varia". Gastropods.com. Retrieved 16 January 2019.