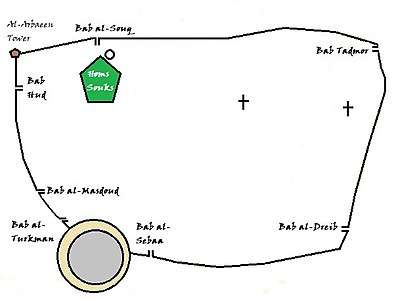
Gates of Homs
The Gates of Homs refer to gates of the city of Homs in central Syria. Historically under the Abbasid dynasty, the city had seven gates.[1] They were the following:
- Bab al-Souq (Gate of the Market), thought to have been located on the southwestern corner of the al-Nouri Mosque.
- Bab Tadmur (Gate of Palmyra) located on the northeastern side of the wall.
- Bab al-Dirayb (or Bab al-Dayr) located on the eastern side of the wall.
- Bab al-Sebaa (Gate of the Lions) located east of the citadel, and leads to the Old City.
- Bab al-Turkman (Gate of the Turkmen) located on the northwestern corner of the citadel at a point where it intersects with the walls.
- Bab al-Masdoud (Closed Door) located to the north of Bab al-Turkman.
- Bab Hud (The Gate of Hud), named after the mausoleum of the prophet Hud, which lies just south of the gate.
| Old City of Homs |
|---|
The Ottomans tore down most of the gates in the 19th century. Only three gates (Bab Tadmor, Bab Hud and Bab al-Dreib) and a small strip of the city walls remain intact.[2]
References
- Dumper (2007) p.173, Dumper, Michael; Stanley, Bruce E.; Abu-Lughod, Janet L. (2007). Cities of the Middle East and North Africa: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-919-5.
- "Homs". HomsOnline. 2008. Retrieved 2009-02-26.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.