Gartland classification
The Gartland classification is a system of categorizing supracondylar humerus fractures, clinically useful as it predicts the likelihood of associated neurovascular injury, such as anterior interosseous nerve neurapraxia or brachial artery disruption.
Classification
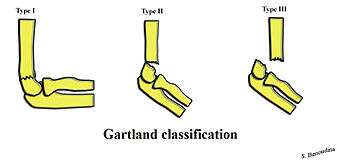
Supracondylar fractures: Gartland classification
| Type³ | Description[1] |
|---|---|
| I | Non-displaced |
| II | Angulated with intact posterior cortex |
| IIA | Angulation |
| IIB | Angulation with rotation |
| III | Complete displacement but have perisosteal (medial/lateral) contact |
| IIIA | Medial periosteal hinge intact. Distal fragment goes posteromedially |
| IIIB | Lateral periosteal hinge intact. Distal fragment goes posterolaterally |
| IV | Periostial disruption with instability in both flexion and extension |
gollark: I have a bunch of stuff for useless cool-looking UIs...
gollark: I don't think it has any support except via comparators.
gollark: Who are you asking?
gollark: Fortunately it goes over websockets since who likes modems anyway, so I can port it fine.
gollark: Unfortunately all my networking infrastructure works with CConly.
References
- Vineet, Kumar; Ajai, Singh (1 December 2016). "Fracture Supracondylar Humerus: A Review". Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 10 (12): 1–6. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/21647.8942. PMC 5296534. PMID 28208961.
Further reading
- Otsuka, N. Y; Kasser, J. R (1997). "Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children". The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 5 (1): 19–26. PMID 10797204.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.