Gardiquimod
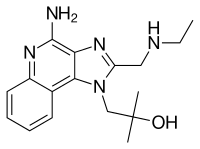
Gardiquimod is an experimental drug which acts selectively at both mouse and human forms of toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7). It functions as an immune response modifier.[1][2][3] The core structure is 1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinoline, as found in related drugs such as imiquimod and resiquimod. It is structurally very similar to resiquimod differing only by an oxygen for nitrogen switch.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.233.311 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H23N5O |
| Molar mass | 313.405 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- Ma F, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhang C (September 2010). "The TLR7 agonists imiquimod and gardiquimod improve DC-based immunotherapy for melanoma in mice". Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 7 (5): 381–8. doi:10.1038/cmi.2010.30. PMC 4002679. PMID 20543857.
- Buitendijk M, Eszterhas SK, Howell AL (June 2013). "Gardiquimod: a Toll-like receptor-7 agonist that inhibits HIV type 1 infection of human macrophages and activated T cells". AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses. 29 (6): 907–18. doi:10.1089/aid.2012.0313. PMC 3653394. PMID 23316755.
- Ma F, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhang C (September 2010). "The TLR7 agonists imiquimod and gardiquimod improve DC-based immunotherapy for melanoma in mice". Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 7 (5): 381–8. doi:10.1038/cmi.2010.30. PMC 4002679. PMID 20543857.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.