GTPBP6
GTP binding protein 6 also known as GTPBP6 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the pseudoautosomal GTPBP6 gene.[5]
| GTPBP6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | GTPBP6, PGPL, GTP binding protein 6 (putative) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 300124 MGI: 1306825 HomoloGene: 8157 GeneCards: GTPBP6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
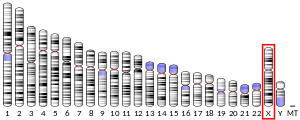
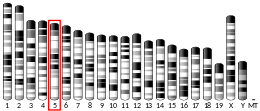
| Location (UCSC) | Chr X: 0.3 – 0.32 Mb | Chr 5: 110.1 – 110.11 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinical significance
Overexpression of GTPBP6 as a result of Klinefelter's syndrome (one or more extra X-chromosomes) is inversely correlated with verbal ability.[6]
gollark: Also, typing speed isn't really a massive issue most of the time *anyway*, as long as you can type decently fast.
gollark: Not necessarily. It makes it easier to type with both hands, which is faster.
gollark: Is that meant to be Karl Marx in the background?
gollark: It was designed to spread out keys which were used together, not limit typing speed.
gollark: Plus, coal plants pollute horribly, which is not very good for or people's health and long term things.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000178605 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000033434 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Gianfrancesco F, Esposito T, Montanini L, Ciccodicola A, Mumm S, Mazzarella R, Rao E, Giglio S, Rappold G, Forabosco A (March 1998). "A novel pseudoautosomal gene encoding a putative GTP-binding protein resides in the vicinity of the Xp/Yp telomere". Hum. Mol. Genet. 7 (3): 407–14. doi:10.1093/hmg/7.3.407. PMID 9466997.
- Vawter MP, Harvey PD, DeLisi LE (September 2007). "Dysregulation of X-Linked Gene Expression in Klinefelter's Syndrome and Association With Verbal Cognition". Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 144B (6): 728–34. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30454. PMC 2094046. PMID 17347996.
Further reading
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.