GMCL1
Germ cell-less, spermatogenesis associated 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GMCL1 gene. [5]
| GMCL1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | GMCL1, BTBD13, GCL, GCL1, SPATA29, germ cell-less, spermatogenesis associated 1, germ cell-less 1, spermatogenesis associated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1345156 HomoloGene: 8021 GeneCards: GMCL1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
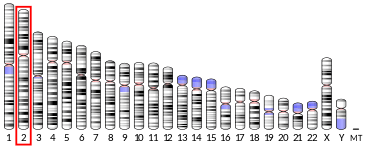
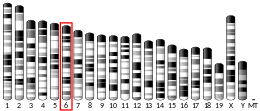
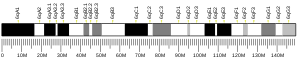
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2: 69.83 – 69.88 Mb | Chr 6: 86.69 – 86.73 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function
This gene encodes a nuclear envelope protein that appears to be involved in spermatogenesis, either directly or by influencing genes that play a more direct role in the process. This multi-exon locus is the homolog of the mouse and drosophila germ cell-less gene but the human genome also contains a single-exon locus on chromosome 5 that contains an open reading frame capable of encoding a highly related protein.
gollark: ++tel init_webhook
gollark: ++tel init_webhook
gollark: Okay, beeing.
gollark: Oops.
gollark: Oh, I see, outdated code.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000087338 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000001157 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: Germ cell-less, spermatogenesis associated 1". Retrieved 2015-09-17.
Further reading
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.