GCaMP
GCaMP is a genetically encoded calcium indicator, or GECI initially developed by Junichi Nakai.[1] GCaMP is created from a fusion of green fluorescent protein (GFP), calmodulin, and M13, a peptide sequence from myosin light chain kinase. The advantage of GECI's is that they can be genetically specified for studies in living organisms. The first transgenic mouse expressing a GCaMP was reported in 2004 [2] and GCaMP was subsequently improved to GCaMP2, which was stable at mammalian body temperatures and enabled the first in vivo mammalian recordings using a GECI.[3] GCaMPs have been subsequently modified to progressively improve the range of the fluorescence signal, resulting in GCaMP3[4] through GCaMP-X.[5] Additionally, red fluorescence GECIs, termed "RCaMPs"[6] have been developed to expand the spectral options for multi-lineage imaging.[7]
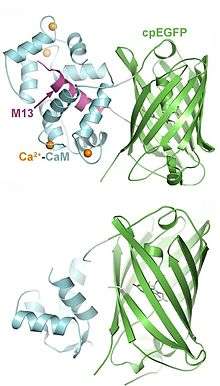
GFP is circularly permutated so that the N- and C-termini are fused, creating a new terminus in the middle of the protein. Fused to the new terminus is calmodulin (CaM) and the M13 domain of a myosin light chain kinase. Calmodulin is a symmetrical, hinge-like protein that binds to four calcium ions via E-F motifs. When calcium is present, CaM undergoes a conformational change, and the hinge region is able to bind helical peptide chains on target proteins, such as M13. In the absence of calcium, the circularly permutated fluorescent proteins exist in a poorly fluorescent state due to a water pathway that enables protonation of the chromophore and poor absorbance at the excitation wavelengths. Ca2+ binding to the calmodulin moiety results in a structural shift that eliminates this solvent pathway, rapid de-protonation of the chromophore, and bright fluorescence.[8][9]
See also
References
- Nakai J, Ohkura M, Imoto K (February 2001). "A high signal-to-noise Ca(2+) probe composed of a single green fluorescent protein". Nature Biotechnology. 19 (2): 137–41. doi:10.1038/84397. PMID 11175727.
- Ji G, Feldman ME, Deng KY, Greene KS, Wilson J, Lee JC, Johnston RC, Rishniw M, Tallini Y, Zhang J, Wier WG, Blaustein MP, Xin HB, Nakai J, Kotlikoff MI (May 2004). "Ca2+-sensing transgenic mice: postsynaptic signaling in smooth muscle". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (20): 21461–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.m401084200. PMID 14990564.
- Tallini YN, Ohkura M, Choi BR, Ji G, Imoto K, Doran R, Lee J, Plan P, Wilson J, Xin HB, Sanbe A, Gulick J, Mathai J, Robbins J, Salama G, Nakai J, Kotlikoff MI (March 2006). "Imaging cellular signals in the heart in vivo: Cardiac expression of the high-signal Ca2+ indicator GCaMP2". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 103 (12): 4753–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0509378103. PMC 1450242. PMID 16537386.
- Tian L, Hires SA, Mao T, Huber D, Chiappe ME, Chalasani SH, Petreanu L, Akerboom J, McKinney SA, Schreiter ER, Bargmann CI, Jayaraman V, Svoboda K, Looger LL (December 2009). "Imaging neural activity in worms, flies and mice with improved GCaMP calcium indicators". Nature Methods. 6 (12): 875–81. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1398. PMC 2858873. PMID 19898485.
- Yang, Yaxiong; Liu, Nan; He, Yuanyuan; Liu, Yuxia; Ge, Lin; Zou, Linzhi; Song, Sen; Xiong, Wei; Liu, Xiaodong (2018-04-17). "Improved calcium sensor GCaMP-X overcomes the calcium channel perturbations induced by the calmodulin in GCaMP". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 1–18. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03719-6. ISSN 2041-1723.
- Akerboom J, Carreras Calderón N, Tian L, Wabnig S, Prigge M, Tolö J, Gordus A, Orger MB, Severi KE, Macklin JJ, Patel R, Pulver SR, Wardill TJ, Fischer E, Schüler C, Chen TW, Sarkisyan KS, Marvin JS, Bargmann CI, Kim DS, Kügler S, Lagnado L, Hegemann P, Gottschalk A, Schreiter ER, Looger LL (2013). "Genetically encoded calcium indicators for multi-color neural activity imaging and combination with optogenetics". Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 6: 2. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2013.00002. PMC 3586699. PMID 23459413.
- Zhao Y, Araki S, Wu J, Teramoto T, Chang YF, Nakano M, Abdelfattah AS, Fujiwara M, Ishihara T, Nagai T, Campbell RE (September 2011). "An expanded palette of genetically encoded Ca²⁺ indicators". Science. 333 (6051): 1888–91. doi:10.1126/science.1208592. PMC 3560286. PMID 21903779.
- Wang Q, Shui B, Kotlikoff MI, Sondermann H (December 2008). "Structural basis for calcium sensing by GCaMP2". Structure. 16 (12): 1817–27. doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.10.008. PMC 2614139. PMID 19081058.
- Akerboom J, Rivera JD, Guilbe MM, Malavé EC, Hernandez HH, Tian L, Hires SA, Marvin JS, Looger LL, Schreiter ER (March 2009). "Crystal structures of the GCaMP calcium sensor reveal the mechanism of fluorescence signal change and aid rational design". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (10): 6455–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.m807657200. PMC 2649101. PMID 19098007.