Functional agrobiodiversity
Biodiversity on the scale of agricultural fields or landscapes, which provides ecosystem services that support sustainable agricultural production and can also have a positive spin-off to the regional and global environment and society as a whole.
Functional agrobiodiversity conceptual diagram
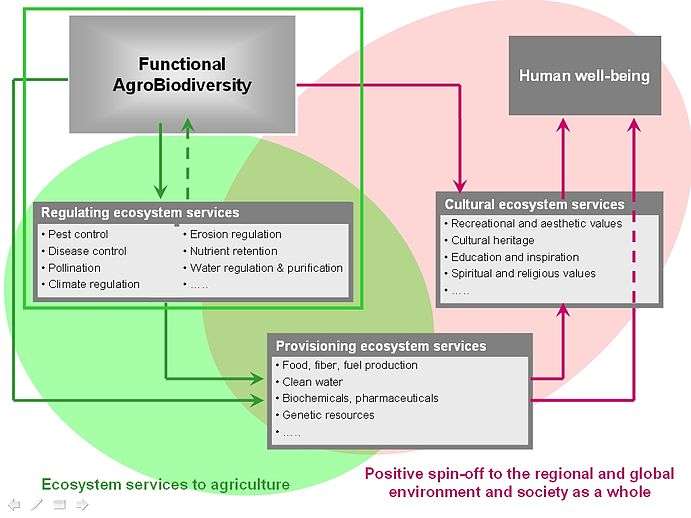
Functional AgroBiodiversity provides regulating, provisioning and cultural ecosystem services that are essential for human well-being. Positive synergies often exist among regulating, provisioning and cultural services and with biodiversity conservation as can be seen from this conceptual diagram. The green area in the diagram highlights the core focus of the European Learning Network. The red area highlights positive spin-off of Functional AgroBiodiversity to the local (e.g. water quality, recreation) and global environment (e.g. climate change) and society as a whole. The graph is adapted from the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005). Supporting services are not included as they are not directly used by the people.
Recently, a project has been initiated which is called 'European Learning Network on Functional AgroBiodiversity', of which the secretariat is held by ECNC. The goal of this network is to exchange knowledge and experience between across country and language borders and between different actors within the field of Functional AgroBiodiversity.