Frank Cable
Frank Taylor Cable (19 June 1863 – 21 May 1945) was an early pioneer in submarine development and piloted the first United States Navy submarine, USS Holland during its pre-commissioning trials.
Frank Taylor Cable | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | June 19, 1863 New Milford, Connecticut, U.S. |
| Died | May 21, 1945 (aged 81) New London, Connecticut, U.S. |
| Occupation | naval architect |
| Spouse(s) | Nettie A. Hungerford |
Early life and education
Cable was born in New Milford, Connecticut, where his father was a farmer. He attended Claverack College in Hudson, New York, followed by Franklin Institute and Drexel Institute in Philadelphia.
Career
Cable was employed by the Electro-Dynamic Company owned by financier Isaac Rice and William Woodnut Griscom. Rice was a financial supporter of inventor John Phillip Holland, whose Holland Torpedo Boat Company (the forerunner and precursor to the Electric Boat Division of General Dynamics Corporation) was developing a prototype submarine, Holland VI, for the United States Navy.
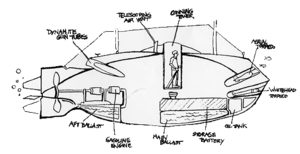
When Holland VI accidentally sank with its hatches open in New York harbor on 13 October 1897,[1] Cable was dispatched by Rice to assist with the repairs. The submarine's internal components had been flooded with corrosive salt water, leading to short circuits and corrosion. Cable had previously specialized in the design and production of propulsion machinery, including diesel engines and electric motors and was able to co-ordinate repair work and restore the submarine's operations.
Cable was retained as an electrician at Holland's company[1] — while still working for Rice — and made a number of changes to the submarine design. A key proposal of Cable's was to improve the submarine's handling by relocating the rudder and stern diving planes aft the propeller.[1] The proposal was accepted and by 4 July 1898 Holland VI was ready for sea trials. Cable was chosen as the civilian trial captain and successfully commanded the vessel during its early operations. Holland VI was purchased by the United States Navy on 11 April 1900 with the initial designation of USS Holland and the subsequent designation of SS-1. The craft was officially commissioned into U.S. Navy service on 12 October 1900. In 1902, Cable supervised the building of five submarines in England. Following the commissioning of USS Holland, Cable was engaged to train prospective submarine crews in Britain, Japan and Russia.[1]
Upon his return to the United States in 1905, he went on to become a co-founder of the Electric Boat Company, based in Groton, Connecticut, the primary manufacturer of United States submarines. He was appointed company general manager in 1930 and died in 1945. Cable worked for Electric Boat for nearly 45 years.
In 1910, Frank Cable and former Navy officer Lawrence Y. Spear organized the New London Ship and Engine Company (NELSECO) to build the diesel engines for the Navy's D and E class submarines. The NELSECO plant was located on the eastern bank of the Thames River in Groton, Connecticut where the General Dynamics Electric Boat Division yard is today (2018). Cable served as the vice-president and general manager of NELSECO until its merger with Electric Boat in 1930. Cable was appointed general manager of Electric Boat following the merger.
Cable lived in New London, Connecticut until his death on 21 May 1945, at the age of 81.
_and_USS_Frank_Cable_(AS-40)_at_Apra_Harbor%2C_Guam%2C_on_23_May_2002_(6640652).jpg)
In 1978, the submarine tender USS Frank Cable was named in his honour.
References
- Mitchell, Robert; Dembek, Stephen (2001-03-03). "Submarine Pioneers". Chief of Naval Operations, Submarine Warfare Division, United States Navy. Archived from the original on 2015-06-12. Retrieved 2008-02-12.
Further reading
- Morris, Richard Knowles (October 1998). "Who Built Those Subs?". Naval History. United States Naval Institute. 12 (5). ISSN 1042-1920. OCLC 16311980.
- Cable, Frank T.; Holland, John Phillip; Kimball, William Wirt (1924). The Birth and Development of the American Submarine. New York: Harper & Bros. OCLC 1729052.
External links
- History of The Electric Boat Company and Frank Cable's role therein. https://web.archive.org/web/20061016074338/http://www.gdeb.com/about/centennial/eb-100yrs-2.html
- Original site of operations for Electric Boat Company was at Crescent Shipyard, Elizabethport, New Jersey. http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/facility/crescent.htm
- "Frank Taylor Cable", Gary McCue, 1999