Follicular hyperplasia
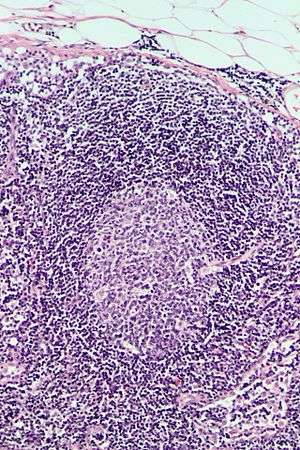
Follicular hyperplasia is a type of lymphoid hyperplasia. It is caused by a stimulation of the B cell compartment.[1] It is caused by an abnormal proliferation of secondary follicles and occurs principally in the cortex without broaching the lymph node capsule. The follicles are cytologically polymorphous, are often polarized, and vary in size and shape.[2] Follicular hyperplasia is distinguished from follicular lymphoma in its polyclonality and lack of bcl-2 protein expression, whereas follicular lymphoma is monoclonal, and does express bcl-2[3]).
| Follicular hyperplasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Reactive follicular hyperplasia, Lymphoid nodular hyperplasia |
 | |
Causes
Some specific reactive lymphadenopathies with a predominantly follicular pattern:[4]
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sjögren syndrome
- IgG4-related disease (IgG4-related lymphadenopathy) [5]
- Kimura disease
- Toxoplasmosis
- Syphilis
- Castleman disease
- Progressive transformation of germinal centers (PTGC)
Diagnosis
Treatment
gollark: That would also spam the server logs.
gollark: `IgjuLVkKGYiyDIckqY_7`
gollark: I'm not going to quote it because it would then flag me for blasphemy too.
gollark: https://osmarks.tk/wsthing/admin/report/143
gollark: Okay, that was a false negative.
References
- Weiss, L. M.; O'Malley, D (2013). "Benign lymphadenopathies". Modern Pathology. 26 Suppl 1: S88–96. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2012.176. PMID 23281438.
- Drew, Torigan; et al. (2001). "Lymphoid hyperplasia of stomach". American Journal of Roentgenology. 177 (1): 71–75. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770071. PMID 11418401.
- Sattar, Husain (2016). Fundamentals of Pathology. Chicago. ISBN 9780983224624.
- Weiss, L. M.; O'Malley, D (2013). "Benign lymphadenopathies". Modern Pathology. 26 Suppl 1: S88–96. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2012.176. PMID 23281438.
- John H. Stone; Arezou Khosroshahi; Vikram Deshpande; et al. (October 2012). "Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations". Arthritis & Rheumatism. 64 (10): 3061–3067. doi:10.1002/art.34593. PMC 5963880. PMID 22736240.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.