Fischer–Hepp rearrangement
The Fischer–Hepp rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in which an aromatic N-nitroso or nitrosamine converts to a carbon nitroso compound:[1][2]
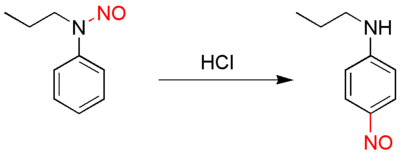
Fischer-Hepp rearrangement
| Fischer-Hepp rearrangement | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Otto Fischer Eduard Hepp |
| Reaction type | Rearrangement reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000095 |
This organic reaction was first described by the German chemist Otto Philipp Fischer (1852–1932 ) and Eduard Hepp (June 11, 1851 – June 18, 1917) [3] in 1886, and is of importance because para-NO secondary anilines cannot be prepared in a direct reaction.
The rearrangement reaction takes place by reacting the nitrosamine precursor with hydrochloric acid. The chemical yield is generally good under these conditions, but often much poorer if a different acid is used. The exact reaction mechanism is unknown but there is evidence suggesting an intramolecular reaction.
Sources
gollark: ...
gollark: Wrong.
gollark: Is this comprehensive enough for you?
gollark: Hold on while I retrieve the documentation.
gollark: You're interviewing for GTech™, you *really* should know basic metaapioinfocryomemetics.
See also
- Friedel–Crafts alkylation-like reactions:
- Hofmann-Martius rearrangement
- Fries rearrangement
References
- O Fischer, E Hepp. Ber Deutsch chem Ges 19 (1886) p2991
- M B Smith, J March. March's Advanced Organic Chemistry (Wiley, 2001) (ISBN 0-471-58589-0)
- W Pötsch. Lexikon bedeutender Chemiker (VEB Bibliographisches Institut Leipzig, 1989) ISBN 3817110553
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.