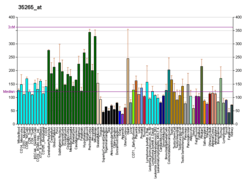
FXR2
Fragile X mental retardation syndrome-related protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FXR2 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is an RNA binding protein containing two KH domains and one RCG box, which is similar to FMRP and FXR1. It associates with polyribosomes, predominantly with 60S large ribosomal subunits. This encoded protein may self-associate or interact with FMRP and FXR1. It may have a role in the development of fragile X mental retardation syndrome.[7]
Interactions
FXR2 has been shown to interact with:
gollark: I'm pretty sure they still have a battery life on the order of days, and not years.
gollark: I see.
gollark: Most smartwatches also seem to not even be able to run always-on displays, at least without consuming 999999 battery.
gollark: Cool, very haptic.
gollark: Circular screens? Ew.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000129245 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000018765 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Zhang Y, O'Connor JP, Siomi MC, Srinivasan S, Dutra A, Nussbaum RL, Dreyfuss G (Nov 1995). "The fragile X mental retardation syndrome protein interacts with novel homologs FXR1 and FXR2". The EMBO Journal. 14 (21): 5358–66. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00220.x. PMC 394645. PMID 7489725.
- Tamanini F, Willemsen R, van Unen L, Bontekoe C, Galjaard H, Oostra BA, Hoogeveen AT (Aug 1997). "Differential expression of FMR1, FXR1 and FXR2 proteins in human brain and testis". Human Molecular Genetics. 6 (8): 1315–22. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.8.1315. PMID 9259278.
- "Entrez Gene: FXR2 fragile X mental retardation, autosomal homolog 2".
- Schenck A, Bardoni B, Moro A, Bagni C, Mandel JL (Jul 2001). "A highly conserved protein family interacting with the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) and displaying selective interactions with FMRP-related proteins FXR1P and FXR2P". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (15): 8844–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.151231598. PMC 37523. PMID 11438699.
- Siomi MC, Zhang Y, Siomi H, Dreyfuss G (Jul 1996). "Specific sequences in the fragile X syndrome protein FMR1 and the FXR proteins mediate their binding to 60S ribosomal subunits and the interactions among them". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 16 (7): 3825–32. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.7.3825. PMC 231379. PMID 8668200.
- Ceman S, Brown V, Warren ST (Dec 1999). "Isolation of an FMRP-associated messenger ribonucleoprotein particle and identification of nucleolin and the fragile X-related proteins as components of the complex". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (12): 7925–32. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.12.7925. PMC 84877. PMID 10567518.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
Further reading
- Siomi MC, Zhang Y, Siomi H, Dreyfuss G (Jul 1996). "Specific sequences in the fragile X syndrome protein FMR1 and the FXR proteins mediate their binding to 60S ribosomal subunits and the interactions among them". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 16 (7): 3825–32. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.7.3825. PMC 231379. PMID 8668200.
- Joseph DR (Jan 1998). "The rat androgen-binding protein (ABP/SHBG) gene contains triplet repeats similar to unstable triplets: evidence that the ABP/SHBG and the fragile X-related 2 genes overlap". Steroids. 63 (1): 2–4. doi:10.1016/S0039-128X(97)00087-1. PMID 9437788.
- Tamanini F, Bontekoe C, Bakker CE, van Unen L, Anar B, Willemsen R, Yoshida M, Galjaard H, Oostra BA, Hoogeveen AT (May 1999). "Different targets for the fragile X-related proteins revealed by their distinct nuclear localizations". Human Molecular Genetics. 8 (5): 863–9. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.5.863. PMID 10196376.
- Bardoni B, Schenck A, Mandel JL (Dec 1999). "A novel RNA-binding nuclear protein that interacts with the fragile X mental retardation (FMR1) protein". Human Molecular Genetics. 8 (13): 2557–66. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.13.2557. PMID 10556305.
- Ceman S, Brown V, Warren ST (Dec 1999). "Isolation of an FMRP-associated messenger ribonucleoprotein particle and identification of nucleolin and the fragile X-related proteins as components of the complex". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (12): 7925–32. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.12.7925. PMC 84877. PMID 10567518.
- Cousin P, Billotte J, Chaubert P, Shaw P (Jan 2000). "Physical map of 17p13 and the genes adjacent to p53". Genomics. 63 (1): 60–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.6062. PMID 10662545.
- Tamanini F, Kirkpatrick LL, Schonkeren J, van Unen L, Bontekoe C, Bakker C, Nelson DL, Galjaard H, Oostra BA, Hoogeveen AT (Jun 2000). "The fragile X-related proteins FXR1P and FXR2P contain a functional nucleolar-targeting signal equivalent to the HIV-1 regulatory proteins". Human Molecular Genetics. 9 (10): 1487–93. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.10.1487. PMID 10888599.
- Schenck A, Bardoni B, Moro A, Bagni C, Mandel JL (Jul 2001). "A highly conserved protein family interacting with the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) and displaying selective interactions with FMRP-related proteins FXR1P and FXR2P". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (15): 8844–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.151231598. PMC 37523. PMID 11438699.
- Brill LM, Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, Mukherji M, Stettler-Gill M, Peters EC (May 2004). "Robust phosphoproteomic profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation sites from human T cells using immobilized metal affinity chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry. 76 (10): 2763–72. doi:10.1021/ac035352d. PMID 15144186.
- Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, Guo A, Goss VL, Spek EJ, Zhang H, Zha XM, Polakiewicz RD, Comb MJ (Jan 2005). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells". Nature Biotechnology. 23 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1038/nbt1046. PMID 15592455.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, Fisk CJ, Li N, Smolyar A, Hill DE, Barabási AL, Vidal M, Zoghbi HY (May 2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (Nov 2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Molecular Systems Biology. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.