FMN riboswitch
The FMN riboswitch (also known as RFN element) is a highly conserved RNA element that is found frequently in the 5'-untranslated regions of prokaryotic mRNAs that encode for flavin mononucleotide (FMN) biosynthesis and transport proteins.[1][2] This element is a metabolite-dependent riboswitch that directly binds FMN in the absence of proteins.[3] In Bacillus subtilis, the riboswitch controls gene expression by causing premature transcription termination within the 5' untranslated region of the ribDEAHT operon and precluding access to the ribosome-binding site of ypaA mRNA.[3][4]
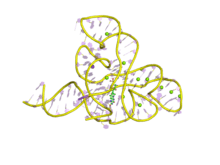
A representation of the 3D structure of the FMN riboswitch. This derived from a crystal structure of the FMN riboswitch bound to FMN.[5]
| FMN riboswitch (RFN element) | |
|---|---|
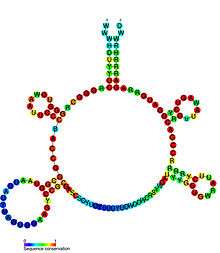 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of FMN | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | FMN |
| Alt. Symbols | RFN |
| Rfam | RF00050 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg; riboswitch |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| GO | 0010181 |
| SO | 0000035 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
References
- Vitreschak AG, Rodionov DA, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS (2002). "Regulation of riboflavin biosynthesis and transport genes in bacteria by transcriptional and translational attenuation". Nucleic Acids Res. 30 (14): 3141–3151. doi:10.1093/nar/gkf433. PMC 135753. PMID 12136096.
- Gelfand MS, Mironov AA, Jomantas J, Kozlov YI, Perumov DA (1999). "A conserved RNA structure element involved in the regulation of bacterial riboflavin synthesis genes". Trends Genet. 15 (11): 439–442. doi:10.1016/S0168-9525(99)01856-9. PMID 10529804.
- Mironov, AS; Gusarov I; Rafikov R; Lopez LE; Shatalin K; Kreneva RA; Perumov DA; Nudler E (2002). "Sensing small molecules by nascent RNA: a mechanism to control transcription in bacteria". Cell. 111 (5): 747–756. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01134-0. PMID 12464185.
- Winkler, WC; Cohen-Chalamish S; Breaker RR (2002). "An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding FMN". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99 (25): 15908–15913. doi:10.1073/pnas.212628899. PMC 138538. PMID 12456892.
- Serganov A, Huang L, Patel DJ (2009). "Coenzyme recognition and gene regulation by a flavin mononucleotide riboswitch". Nature. 458 (7235): 233–237. doi:10.1038/nature07642. PMC 3726715. PMID 19169240.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.