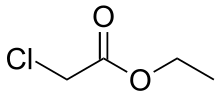
Ethyl chloroacetate
Ethyl chloroacetate is a chemical compound used primarily in the chemical industry. It is used as a solvent for organic synthesis and as an intermediate in the production of pesticides (such as sodium fluoroacetate).[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl chloroacetate | |
| Other names
Ethyl 2-chloroacetate Ethyl monochloroacetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.995 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7ClO2 | |
| Molar mass | 122.55 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.145 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | −26 °C (−15 °F; 247 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 143 °C (289 °F; 416 K)[1] |
| -72.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
An example for the use of this agent was in the synthesis of Cinepazet, respectively.
References
- Ethyl chloroacetate at Sigma-Aldrich
- "Ethyl chloroacetate" (PDF). Risk-Based Prioritization Document. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. April 2009.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.