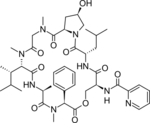
Etamycin
Etamycin, also known as viridogrisein,[1] is a cyclic peptide antibiotic isolate of marine actinomycete.[2] Etamycin was first isolated from a Streptomyces species in 1957 by Lawson and co-workers.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Viridogrisein I, Etamycin A, Neoviridogrisein IV, Antibiotic K-179, Antibiotic F-1370A | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C44H62N8O11 | |
| Molar mass | 879.025 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Notes
- Carcia-Mendoza, C (1965). "Studies on the mode of action of etamycin (viridogrisein)". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects. 97 (2): 394–396. doi:10.1016/0304-4165(65)90121-2. PMID 14292864.
- Haste, Nina M (2010). "Activity of the streptogramin antibiotic etamycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus". The Journal of Antibiotics. 63 (5): 219–224. doi:10.1038/ja.2010.22. PMC 2889693. PMID 20339399.
- Sheehan, John C (1957). "The Structure of Etamycin". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80 (13): 3349–3355. doi:10.1021/ja01546a039.
gollark: PotatOS.
gollark: What?
gollark: Why potatOS sttuuopid??!
gollark: Ah, yes.
gollark: Why would you need thæŧ?
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.