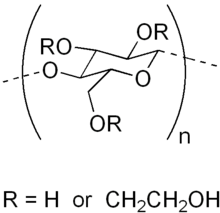
Hydroxyethyl cellulose
Hydroxyethyl cellulose is a gelling and thickening agent derived from cellulose. It is widely used in cosmetics, cleaning solutions, and other household products.[1] Hydroxyethyl cellulose and methyl cellulose are frequently used with hydrophobic drugs in capsule formulations, to improve the drugs' dissolution in the gastrointestinal fluids. This process is known as hydrophilization.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Cellulose, hydroxyethyl ether; Hydroxyethylcellulose; 2-Hydroxyethyl cellulose; Hyetellose; Natrosol; Cellosize | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.116.562 |
| E number | E1525 (additional chemicals) |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| variable | |
| Molar mass | variable |
| Melting point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hydroxyethyl cellulose is also used extensively in the oil & gas industry as a drilling mud additive under the name HEC as well in industrial applications, paint & coatings, ceramics, adhesives, emulsion polymerization, inks, construction, welding rods, pencils and joint fillers.
Hydroxyethyl cellulose is one of the main ingredients in the personal lubricant KY Jelly. It is also a key ingredient in the formation of big bubbles as it possesses the ability to dissolve in water but also provide structural strength to the soap bubble. Among other similar chemicals, it is often used as slime (and gunge, in the UK), a gooey substance often used on television and in fundraising events which is poured over individuals with the aim of causing embarrassment.
References
- Record in the Household Products Database of NLM
- "Natrosol hydroxyethylcellulose". ashland.com. Retrieved 12 May 2018.