Dodeka music notation
The Dodeka Music Notation is an alternative music notation or musical notation system invented and designed in 1980s by inventor and musician Jacques-Daniel Rochat in an attempt to improve upon traditional music notation.
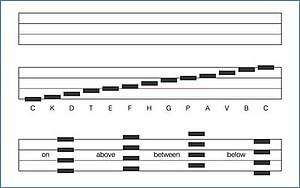
Staff and pitch
Unlike conventional musical notation, the Dodeka music notation system uses a chromatic scale of 12 pitches and follows an equal pitch intervals configuration, with 4 lines per octave.[1][2] In this configuration, the 12 notes of an octave appear in four positions vis-à-vis the staff lines, that is, either on, between, above and below the lines.[2]
Each pitch has its own unique place on the staff. And while conventional music notation may alter notes using accidental signs or key signatures, notes in the Dodeka notation appear as they are. There are no more key signatures or accidental signs in this musical system.

Note duration
The Dodeka notation system represents note duration in a visual manner. Note lengths are represented through the notes graphical shapes, similar to what can be found in sequencer programmes. The reference time unit or time value being the quarter note (or crotchet), all durations are expressed as visual ratios from this reference point.[3] For example, a whole note is the representation of four quarter note lengths. At the opposite, an eighth note (or quaver) is twice as short as a quarter note.
Octaves and clefs
While traditional music notation represents the whole musical spectrum with different clefs, such as the treble or bass clefs, in the Dodeka notation the staff configuration is consistent throughout the octaves. This means that each pitch has its own unique position on the staff regardless of the octaves.[3] For example, a C always keeps its position in every octave.
Relationship with keyboard layout
The Dodeka music notation was developed together with the Dodeka keyboard: an alternative keyboard layout that reflects the notation system. With this keyboard, the relationship between the notes on the sheet music and the keys on the keyboard are direct and consistent thanks to colour references.[1][4]
References
- Kientz, Bertrand (2015). "BIGRAM EDITOR: A SCORE EDITOR FOR THE BIGRAM NOTATION" (PDF). Tenor.
- "Systems with twelve vertical staff positions per octave". The Music Notation Project.
- Rochat, Jacques-Daniel (2018). Dodeka: A Musical Revolution. ISBN 978-2-9701275-0-5.
- Dredge, Stuart (August 15, 2017). "Dodeka rethinks the keyboard… and music notation". Music:ally.
External links
- The Music Notation Project, Introduction to various types of alternative notation systems
- Dodeka Music, Dodeka Music Notation website