Diphenyldichloromethane
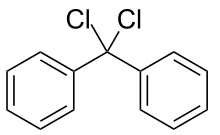
Diphenyldichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CCl2. It is a colorless solid that is used as a precursor to other organic compounds.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1'-(Dichloromethylene)dibenzene | |
| Other names
Dichlorodiphenylmethane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1910601 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.486 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10Cl2 | |
| Molar mass | 237.12 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.235 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 146 to 150 °C (295 to 302 °F; 419 to 423 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 193 °C (379 °F; 466 K) at 32 torr[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
It is prepared from carbon tetrachloride and anhydrous aluminium chloride as catalyst in a double Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene.[3] Alternatively, benzophenone is treated with phosphorus pentachloride:[4]
- (C6H5)2CO + PCl5 → (C6H5)2CCl2 + POCl3
Reactions
It undergoes hydrolysis to benzophenone.[3]
- (C6H5)2CCl2 + H2O → (C6H5)2CO + 2 HCl
It is used in the synthesis of tetraphenylethylene,[5] diphenylmethane imine hydrochloride and benzoic anhydride.[6]
gollark: Yes, those.
gollark: This is a bad reason, consume bees.
gollark: Imagine not coming into existence spontaneously and fully formed via time loops.
gollark: It's when the cults go to war every 1st April.
gollark: Drones, not planes, they don't have to move very fast.
References
- Ballester, Manuel; Juan Riera-Figueras; Juan Castaner; Carlos Badfa; Jose M. Monso (1971). "Inert carbon free radicals. I. Perchlorodiphenylmethyl and perchlorotriphenylmethyl radical series". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 93 (9): 2215–2225. doi:10.1021/ja00738a021. ISSN 0002-7863.
- Andrews, L. J.; W. W. Kaeding (1951). "The Formation of Benzophenone and its Diethylketal in the Ethanolysis of Diphenyldichloromethane". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 73 (3): 1007–1011. doi:10.1021/ja01147a036. ISSN 0002-7863.
- Marvel, C. S.; Sperry, W. M. (1941). "Benzophenone". Organic Syntheses.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collective Volume, 1, p. 95
- Spaggiari, Alberto; Daniele Vaccari; Paolo Davoli; Giovanni Torre; Fabio Prati (2007). "A Mild Synthesis of Vinyl Halides andgem-Dihalides Using Triphenyl Phosphite−Halogen-Based Reagents". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 72 (6): 2216–2219. doi:10.1021/jo061346g. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 17295542.
- Inaba, S (1982). "Metallic nickel as a reagent for the coupling of aromatic and benzylic halides". Tetrahedron Letters. 23 (41): 4215–4216. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)88707-9. ISSN 0040-4039.
- "Preps in which diphenyldichloromethane appears". www.orgsyn.org. Archived from the original on 25 August 2005. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.