Dimethylmagnesium
Dimethylmagnesium is an organomagnesium compound. It is a white pyrophoric solid.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dimethylmagnesium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H6Mg | |
| Molar mass | 54.375 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Reacts | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Like other dialkylmagnesium compounds, it is prepared by adding at least one equivalent of dioxane to a solution of methylmagnesium halide:[1][2]
- 2 CH3MgX + dioxane ⇌ (CH3)2Mg + MgX2(dioxane)
Addition of 0.5 molar equivalents of 1,4-dioxane causes precipitation of MgX2 as an insoluble dioxane-adduct, driving the Schlenk equilibrium to (CH3)2Mg.
It can also be prepared by treating calcium, magnesium and methyl iodide in diethyl ether or by combining dimethyl mercury and magnesium.[3][4]
Properties
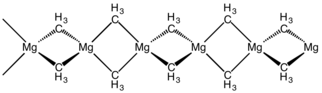
The structure of this compound has been determined by X-ray crystallography. The material is a polymer with the same connectivity as silicon disulfide, featuring tetrahedral magnesium centres, each surrounded by bridging methyl groups. The Mg-C distances are 224 pm.[5] Dimethylberylium adopts the same structure.[6]
References
- Cope, A. C. (1935). "The Preparation of Dialkylmagnesium Compounds from Grignard Reagents". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57 (11): 2238–2240. doi:10.1021/ja01314a059.
- Anteunis, M. (1962). "Studies of the Grignard Reaction. II. Kinetics of the Reaction of Dimethylmagnesium with Benzophenone and of Methylmagnesium Bromide-Magnesium Bromide with Pinacolone". J. Org. Chem. 27 (2): 596–598. doi:10.1021/jo01049a060.
- [, p. 215, at Google Books Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. XIII/2a, 4th Edition Organometallic Compounds of Group II of the Periodic Table (except mercury)] Check
|url=value (help) (in German), Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, p. 215, ISBN 978-3-13-180654-3 - Jane E. Macintyre (1994), [, p. 2273, at Google Books Dictionary of Organometallic Compounds] Check
|url=value (help) (in German), CRC Press, p. 2273, ISBN 978-0-412-43060-2 - Weiss, E. (1964). "Die Kristallstruktur des Dimethylmagnesiums". J. Organomet. Chem. 2 (4): 314–321. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)82217-2.
- Snow, A.I.; Rundle, R.E. (1951). "Structure of Dimethylberyllium". Acta Crystallographica. 4 (4): 348–52. doi:10.1107/S0365110X51001100. hdl:2027/mdp.39015095081207.